Large Pre-trained Language Models Tackle Biological Inference for Rare Tissues with Limited Data
- CancerGPT, a few-shot learning approach, uses LLMs to predict drug pair synergy in rare tissues with limited data.
- Experiments demonstrated significant accuracy in predicting drug pair synergy, even with very few or zero samples.
- First study to utilize an LLM-based prediction model for biological reaction prediction tasks in rare tissues.
A recent study has revealed the potential of large pre-trained language models (LLMs) in the field of biology, particularly for few-shot learning tasks with limited data. The researchers introduced CancerGPT, a model that predicts drug pair synergy in rare tissues that lack structured data and features.
The study involved seven rare tissues from different cancer types, and the CancerGPT model (with ~124M parameters) demonstrated significant accuracy in predicting drug pair synergy, even with very few or zero samples. The results were comparable to the larger fine-tuned GPT-3 model (with ~175B parameters), showcasing the potential of tailoring LLMs to specific tasks for improved prediction accuracy.
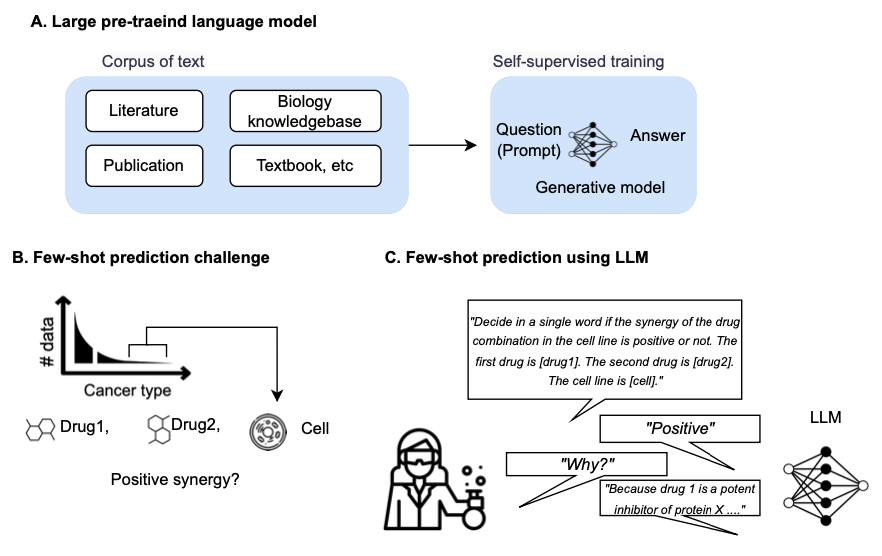
This research marks the first attempt at tackling drug pair synergy prediction in rare tissues using an LLM-based prediction model. The LLM’s reasoning for its predictions revealed that it implicitly infers unseen synergistic effects by combining several independent scientific facts.
Despite these promising results, the study has some limitations. To establish the generalizability of LLMs as “generalist” AI, a wider range of biological prediction tasks must be tested, and the complementary nature of LLM-generated information with existing genomic or chemical features should be investigated. Additionally, the accuracy of the LLM’s arguments cannot always be verified, and further research is needed to ensure its reasoning is grounded in factual evidence.
Regardless of these limitations, the study provides valuable insights into the potential of LLMs as few-shot prediction models in biology and paves the way for future research in this area.
