Approach to Object Segmentation in Videos Using Language Instructions
- Language-Instructed Reasoning: VideoLISA leverages the capabilities of large language models to create temporally consistent segmentation masks in videos, transforming how models interpret language instructions.
- Innovative Techniques: The model integrates a Sparse Dense Sampling strategy and a unique One-Token-Seg-All approach, addressing the complexities of video object segmentation that traditional image-based methods struggle to handle.
- Performance Validation: Extensive evaluations on benchmarks like the new ReasonVOS demonstrate VideoLISA’s superior capabilities in complex reasoning, temporal understanding, and object tracking, highlighting its potential as a unified model for both video and image segmentation.
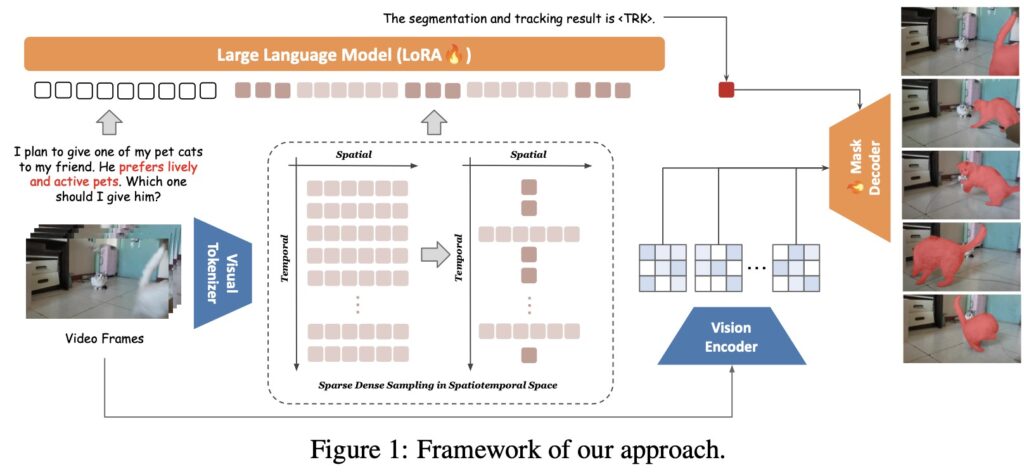
The introduction of VideoLISA marks a significant advancement in the field of video object segmentation (VOS), where traditional image-based approaches have fallen short. With the increasing complexity of visual content, especially in videos, understanding and localizing objects based on human intent has become a pivotal task for intelligent systems. VideoLISA harnesses the power of language as a natural interface, allowing it to accurately identify target objects through user-defined instructions. This model not only enhances interaction but also opens new avenues for video analysis across various applications.
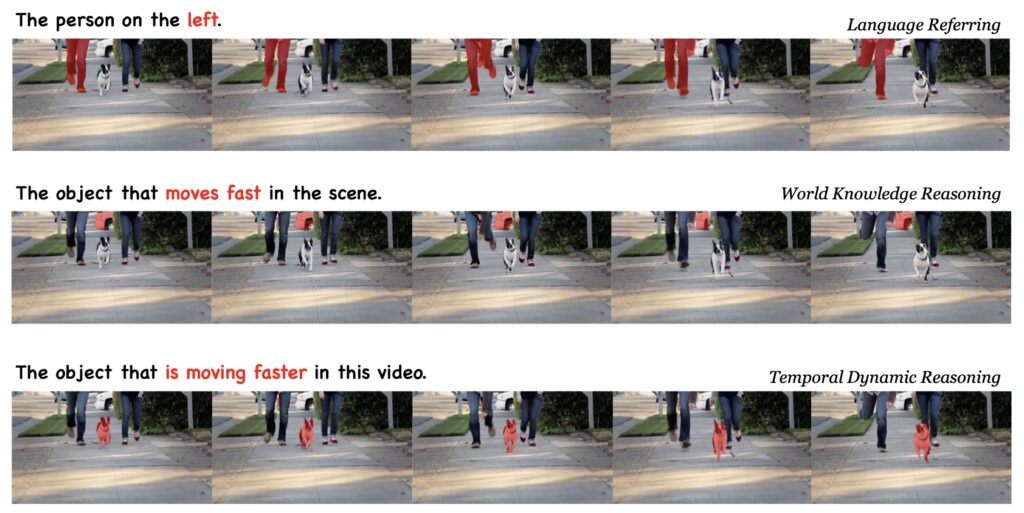
One of the main challenges in VOS is the additional temporal dimension present in video content, which complicates the segmentation process. Unlike static images, videos require models to grasp and predict how objects move and change over time. Existing methods have struggled to maintain consistency across frames, leading to unreliable results. VideoLISA addresses these issues by employing a Sparse Dense Sampling strategy that allows it to effectively capture the temporal dynamics of videos while preserving spatial details. This innovative approach leverages the inherent redundancy found in video frames, resulting in more accurate and contextually aware segmentation.
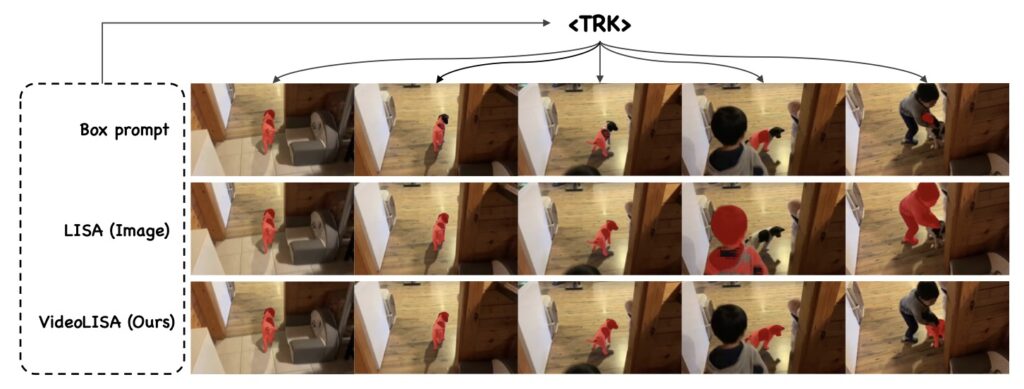
Another groundbreaking feature of VideoLISA is its One-Token-Seg-All approach. By using a specially designed <TRK> token, the model can segment and track objects consistently across multiple frames. This method simplifies the segmentation process by employing a unified prompt, thereby reducing the complexity typically associated with video segmentation tasks. The training objective is tailored to enhance the model’s ability to understand and act upon varying language instructions, making it adaptable to different scenarios and user inputs.
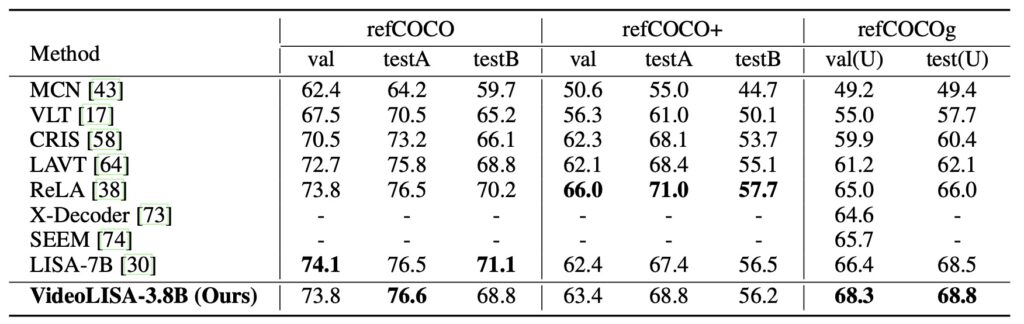
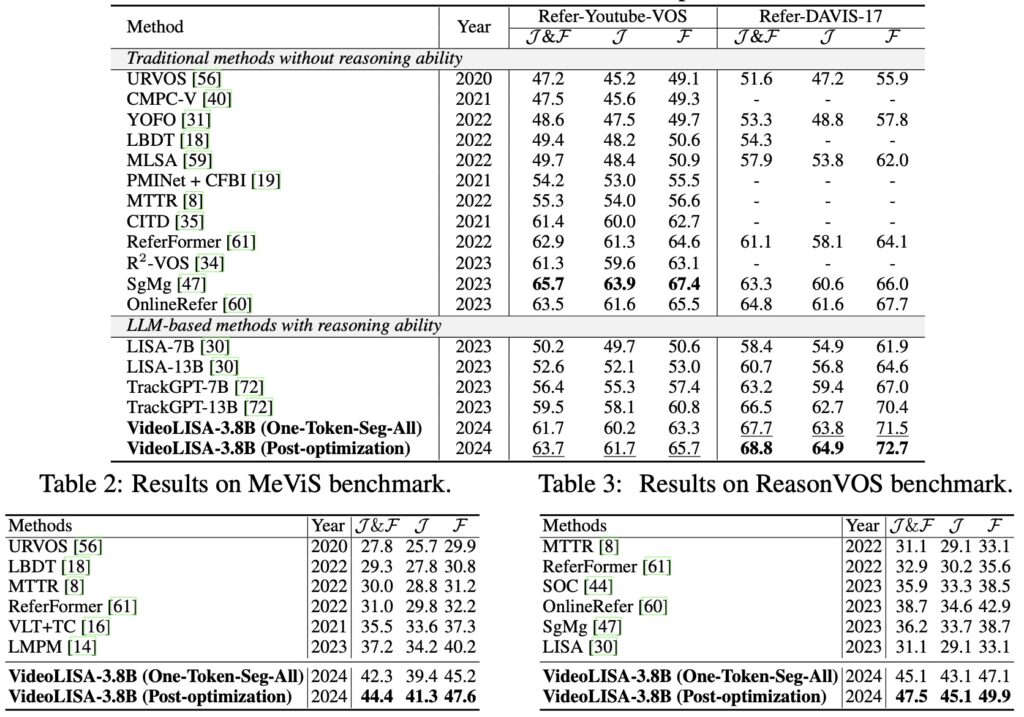
Extensive evaluations have validated VideoLISA’s performance on diverse benchmarks, particularly the newly introduced ReasonVOS benchmark. These assessments showcase the model’s exceptional capabilities in handling complex reasoning tasks and temporal understanding, significantly outperforming existing methods. Notably, VideoLISA also exhibits promising generalization to image segmentation tasks, indicating its potential as a versatile model capable of addressing a broad range of segmentation challenges.
The significance of VideoLISA extends beyond its technical achievements. By bridging the gap between language instructions and video segmentation, this model represents a crucial step toward more intuitive and user-friendly AI systems. As video content continues to proliferate across platforms, the ability to accurately segment and analyze objects based on human intent will empower various industries, from entertainment and education to security and healthcare.

VideoLISA stands at the forefront of a new era in video object segmentation, driven by language-instructed reasoning. With its innovative design and advanced capabilities, the model not only enhances the understanding of dynamic content but also sets the stage for future advancements in AI-driven video analysis. As the landscape of video processing evolves, VideoLISA is poised to become an essential tool for researchers and practitioners alike, enabling them to harness the full potential of language and vision in an increasingly interconnected world.
