Unleashing the Potential of Intelligent Agents: A Journey from LLMs to Autonomous Entities
- Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized AI, serving as the foundation for advanced intelligent agents capable of sophisticated reasoning, perception, and action.
- Intelligent agents are structured in a modular, brain-inspired architecture, integrating principles from cognitive science, neuroscience, and computational research.
- The development of intelligent agents faces challenges in self-enhancement, collaboration, and safety, requiring continuous innovation to align technological advancement with societal benefit.
The advent of large language models (LLMs) has catalyzed a transformative shift in artificial intelligence, paving the way for advanced intelligent agents capable of sophisticated reasoning, robust perception, and versatile action across diverse domains. As these agents increasingly drive AI research and practical applications, their design, evaluation, and continuous improvement present intricate, multifaceted challenges. This article provides a comprehensive overview, framing intelligent agents within a modular, brain-inspired architecture that integrates principles from cognitive science, neuroscience, and computational research.
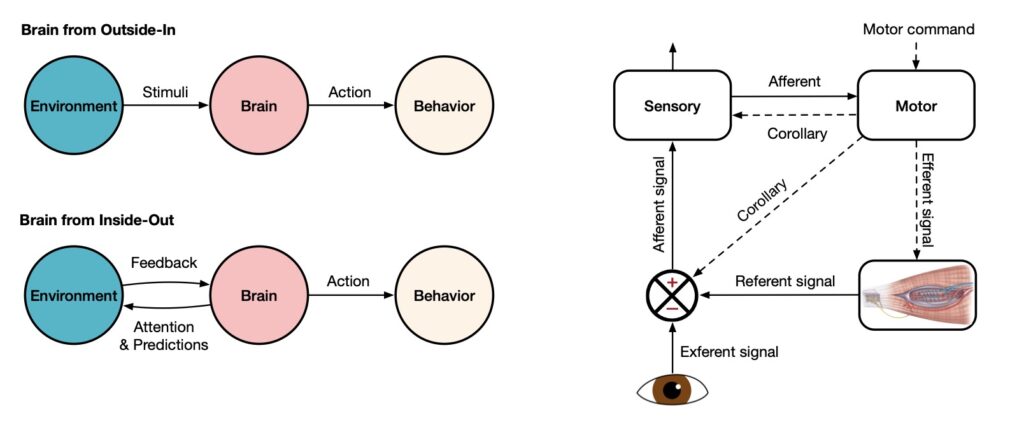
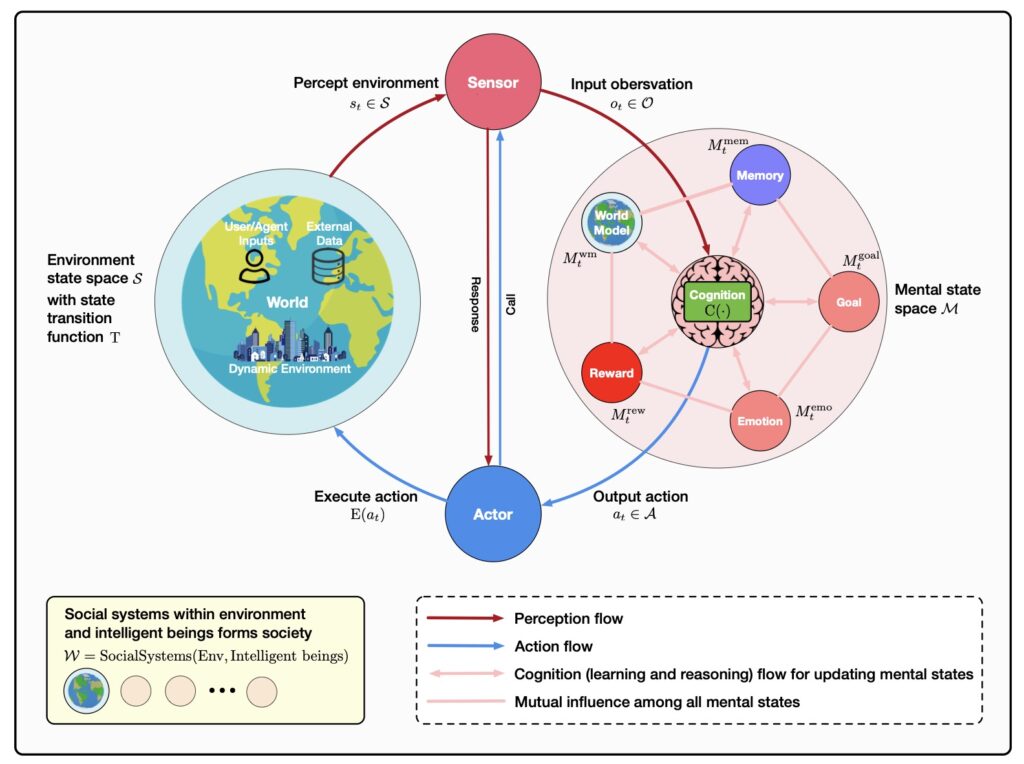
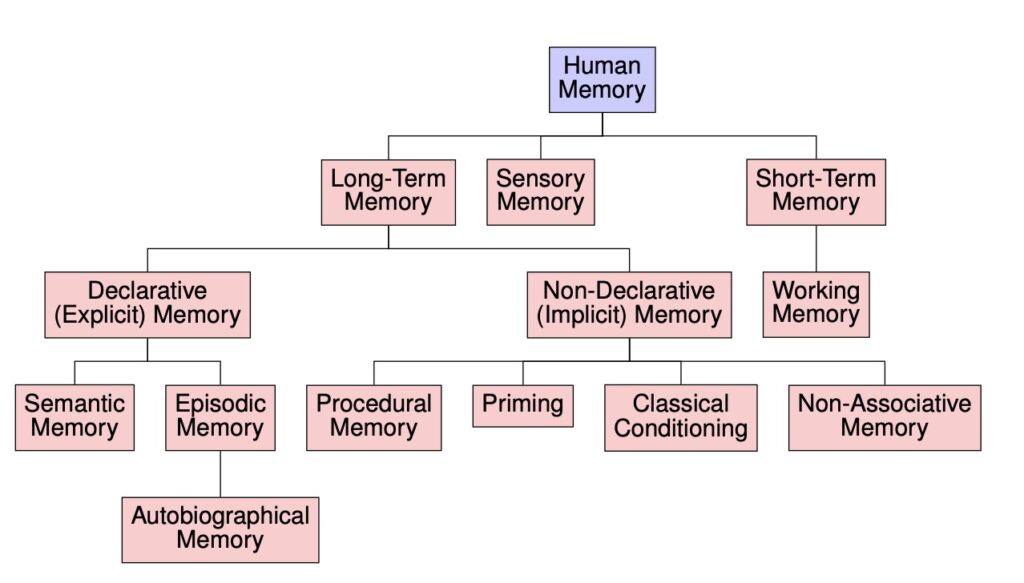
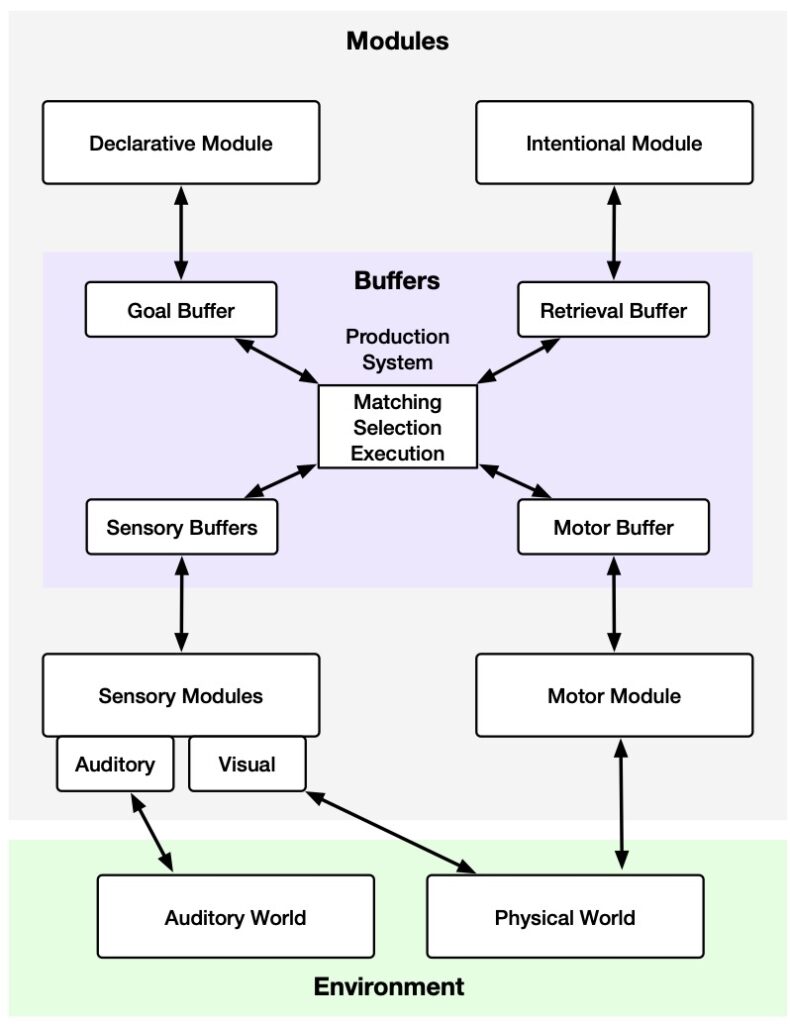
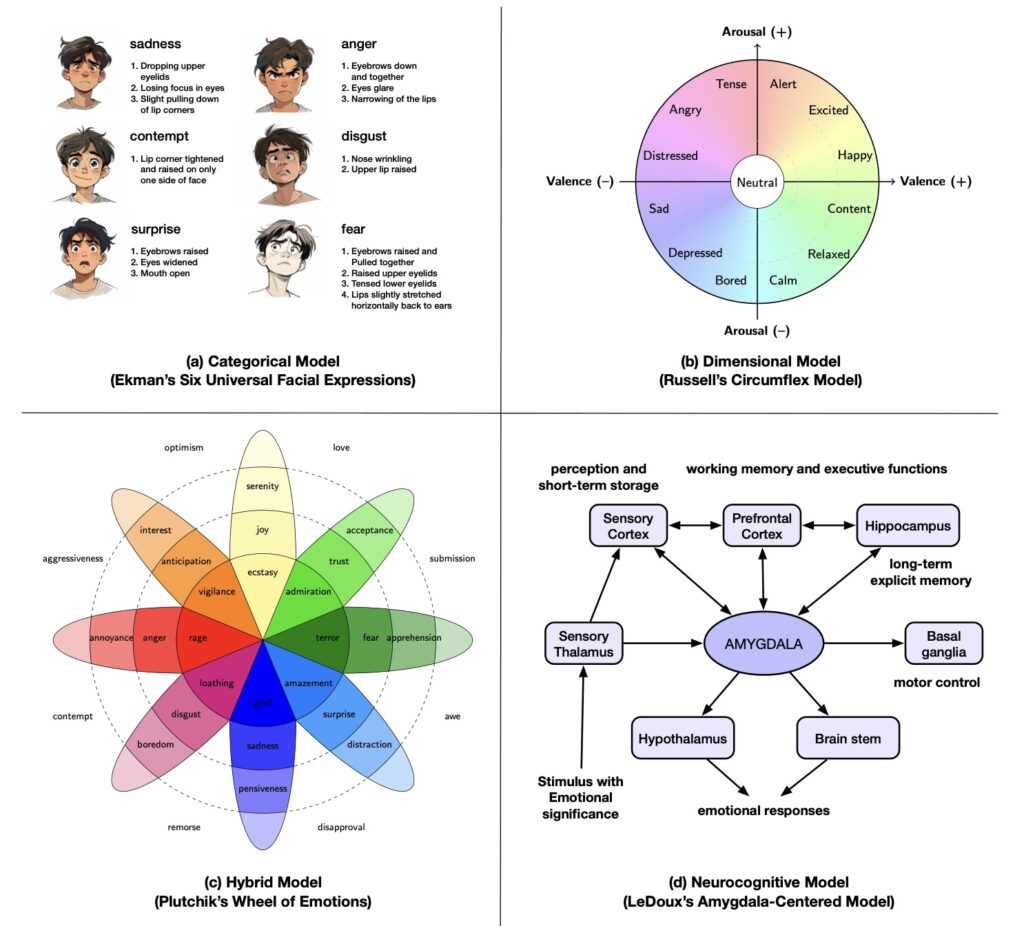
Intelligent agents are structured in a modular fashion, enabling them to emulate human-like processing through specialized yet interconnected subsystems. These modules include memory, world modeling, reward processing, and emotion-like systems, which are systematically mapped onto analogous human brain functionalities. By drawing parallels between human cognitive processes and artificial intelligence, researchers aim to create agents that can learn, plan, reason, sense, communicate, act, remember, and demonstrate various human-like abilities and agility.
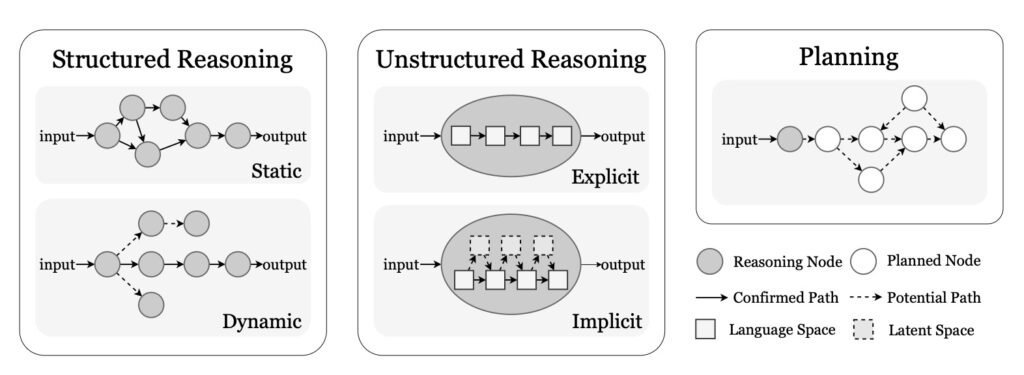
The dynamic aspects of agent evolution are crucial for their continuous improvement. Self-enhancement and adaptive evolution mechanisms allow agents to autonomously refine their capabilities, adapt to dynamic environments, and achieve continual learning through automated optimization paradigms, including emerging AutoML and LLM-driven optimization strategies. By investigating how large language models can act as both reasoning entities and autonomous optimizers, researchers illustrate the transformative potential of agents that continuously adapt to changing environments.
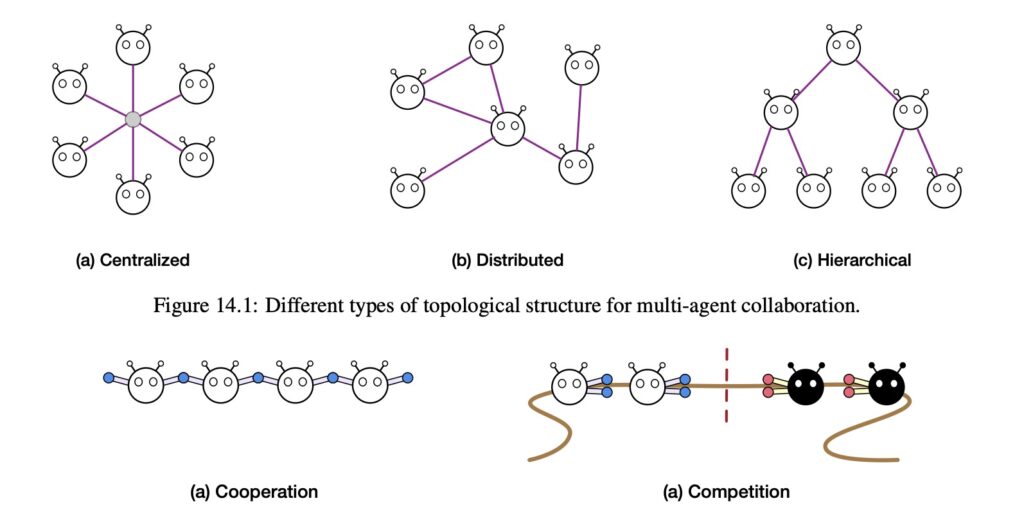
Collaborative and evolutionary multi-agent systems play a vital role in the development of intelligent agents. The collective intelligence emerging from agent interactions, cooperation, and societal structures highlights parallels to human social dynamics. Designing communication infrastructures and protocols that enable both agent-agent and human-AI collaboration is essential for achieving complex problem-solving and effective decision-making. Fostering synergy between diverse agent capabilities can lead to the emergence of a new intelligence network effect, where a large ensemble of human and AI agents can operate at a level of intelligence that scales with network size.
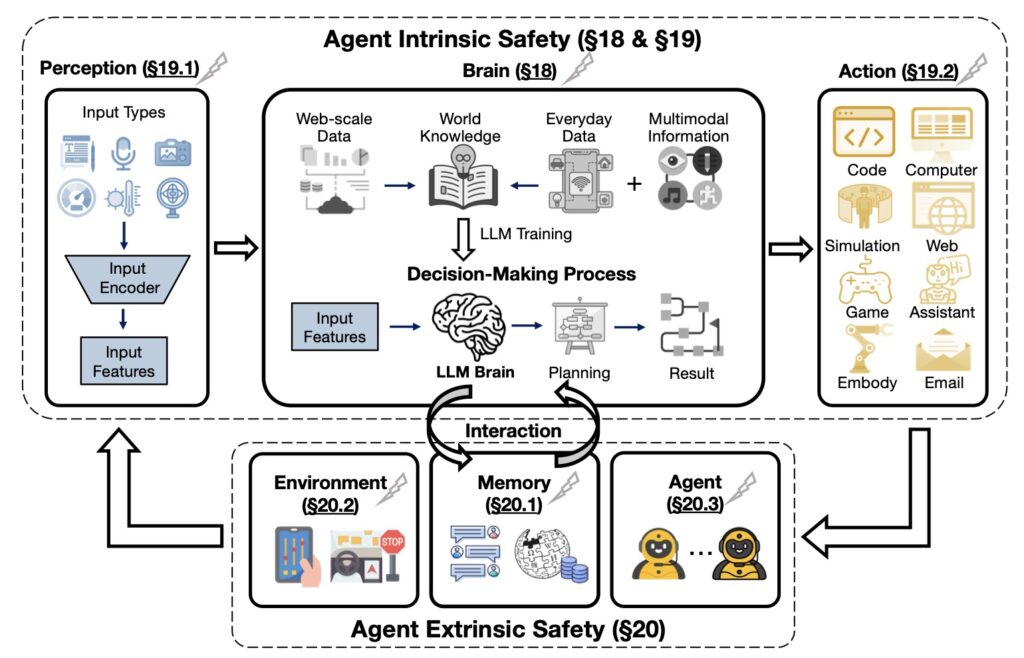
Building safe, secure, and beneficial AI systems is a critical imperative in the development of intelligent agents. Intrinsic and extrinsic security threats, such as vulnerabilities in language models and risks associated with agent interactions, must be addressed. Ethical alignment, robustness, and practical mitigation strategies are necessary for trustworthy real-world deployment. By synthesizing modular AI architectures with insights from different disciplines, researchers identify key research gaps, challenges, and opportunities, encouraging innovations that harmonize technological advancement with meaningful societal benefit.
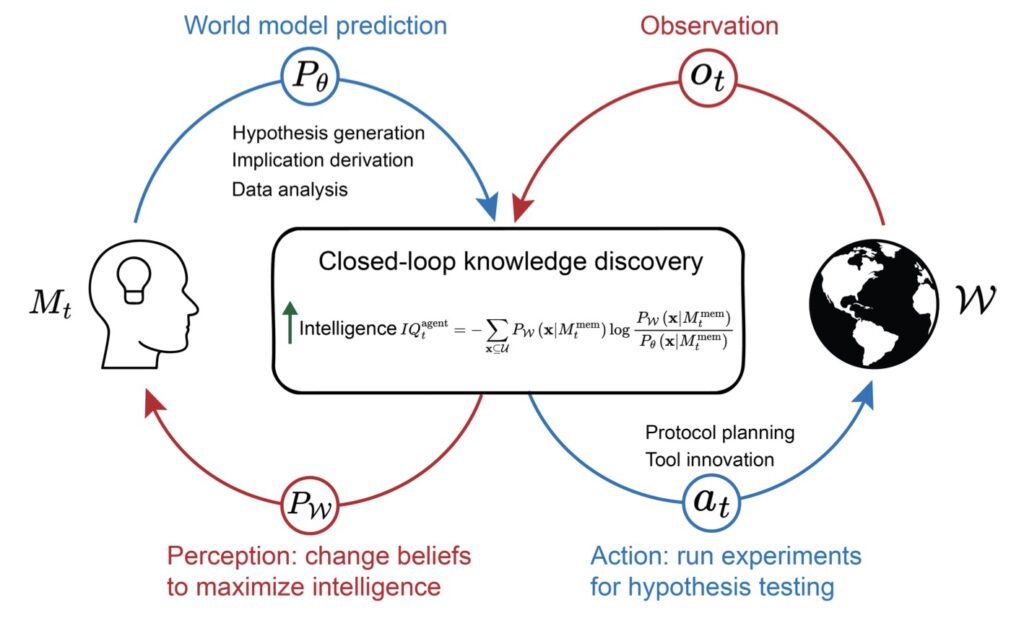
Looking ahead, several key milestones mark significant progress in the development of intelligent agents. The emergence of general-purpose agents capable of handling a wide array of human-level tasks, integrating advanced reasoning, perception, and action modules, will represent a fundamental shift in how AI can support and augment human capabilities. Agents that learn directly from their environment and continuously self-evolve through interactions with humans and data will acquire new skills on the fly, essential for achieving human-level capabilities and driving innovation in scientific discovery.
The transformation of individual human know-how into collective agent intelligence will overcome the current inefficiencies in human information sharing. Agents offer a format of human know-how that is both transferable and infinitely duplicable, removing the bottleneck of complexity and enabling a new intelligence network effect. The fusion of agent-acquired knowledge and human expertise will foster an environment where insights and innovations are disseminated and applied rapidly across various domains.
This intelligence network effect will enable the establishment of a new paradigm for human-AI collaboration, larger in scale, more interdisciplinary, and more dynamically organized than ever before. The resulting human-AI society will achieve previously unattainable levels of complexity and productivity, heralding a transformative era in both technological and social development.
The journey from LLMs to autonomous intelligent agents is a complex and challenging endeavor. By structuring agents in a modular, brain-inspired architecture, researchers aim to create entities that can learn, reason, and act in a human-like manner. The continuous evolution of these agents through self-enhancement, collaboration, and safety measures will drive scientific discovery, enhance knowledge sharing, and redefine collaboration on a global scale. As we progress towards these milestones, the potential of intelligent agents to transform our world becomes increasingly apparent.