AI-powered robots are mastering surgical techniques by watching videos, paving the way for fully autonomous procedures.
- Imitation Learning Breakthrough: Robots are now trained to perform surgical procedures by observing videos of experienced surgeons, leveraging cutting-edge AI techniques.
- Efficiency and Adaptability: Unlike traditional hand-coding methods, imitation learning allows robots to learn new tasks in days, adapting to unforeseen situations in real-time.
- Global Impact: Autonomous surgical robots promise to address the shortage of skilled surgeons, improve precision, and reduce medical errors worldwide.
Robotic surgery has reached a groundbreaking milestone as researchers from Johns Hopkins University and Stanford University developed an AI-powered robot capable of learning surgical skills by simply watching experienced surgeons at work. This advancement marks a major step toward fully autonomous robotic surgery, promising to revolutionize the field of medical robotics.
The innovation leverages imitation learning, a method that enables robots to learn by observing, eliminating the traditional need for painstakingly coding each movement. This not only enhances efficiency but also expands the scope of robotic surgery, offering solutions to long-standing challenges in the field.
Teaching Robots Through Observation
At the heart of this breakthrough is the da Vinci Surgical System, a widely used robotic tool in operating rooms worldwide. Researchers used hundreds of videos recorded by the system’s wrist cameras, training the AI model to mimic three essential surgical tasks: manipulating a needle, lifting tissue, and suturing.
Unlike earlier systems, the AI model translates visual inputs into precise robotic movements using advanced machine learning techniques. “It’s really magical to have this model. We feed it camera input, and it predicts the robotic movements needed for surgery,” said senior author Axel Krieger.
What sets this approach apart is its ability to learn relative movements rather than absolute actions. This adaptability ensures the robot can perform tasks with greater precision, even overcoming errors like dropping a needle mid-procedure.
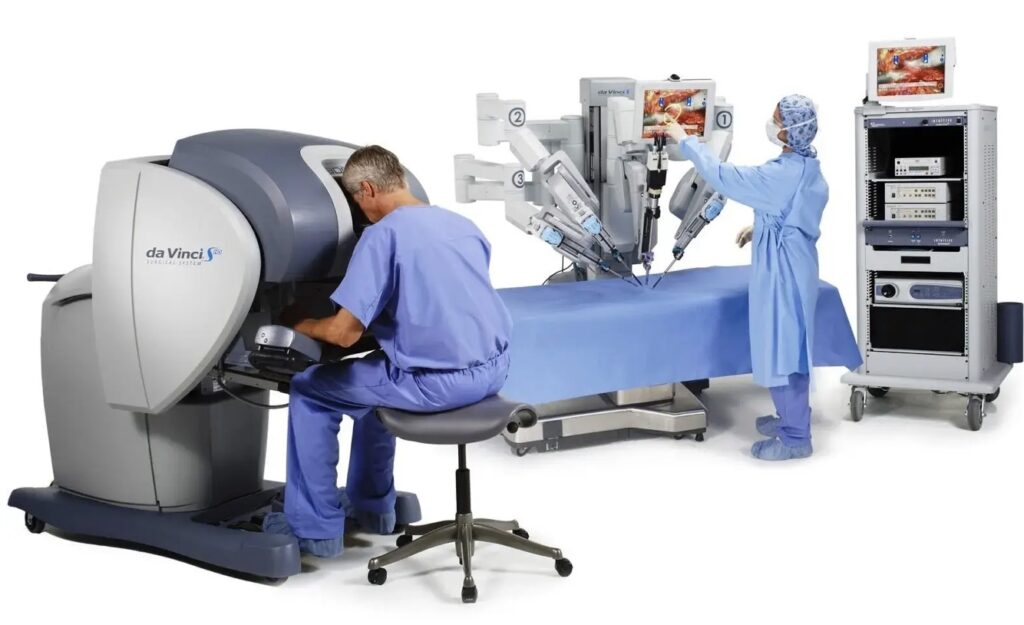
A New Era of Robotic Efficiency
Traditional robotic programming is a slow and resource-intensive process, often requiring years to code a single task. By contrast, the imitation learning model allows robots to master new surgical procedures in just days.
“This advancement allows us to accelerate the goal of autonomy while reducing medical errors and achieving more accurate surgery,” noted Krieger. The AI’s capability to adapt to unfamiliar environments further enhances its reliability and efficiency, making it a game-changer for surgical robotics.
Transforming Global Healthcare
The implications of autonomous robotic surgery extend far beyond efficiency. With a global shortage of skilled surgeons, particularly in underserved regions, AI-powered surgical robots could bridge critical gaps in healthcare. Their precision and consistency promise fewer complications and improved patient outcomes.
As lead author Ji Woong “Brian” Kim explained, “Even with a few hundred demos, the model can learn procedures and adapt to new environments it hasn’t encountered.” This adaptability positions surgical robots as vital tools for addressing the growing demand for advanced healthcare solutions.
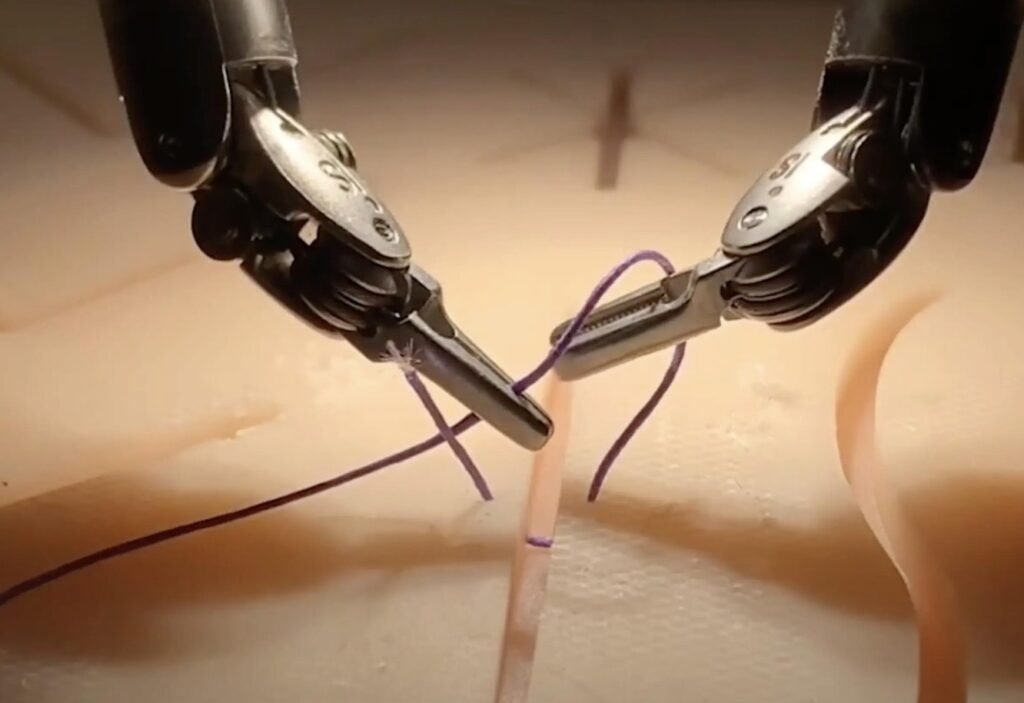
A Vision for the Future
The research team is already working to expand the model’s capabilities, aiming to train robots for complete surgical procedures rather than isolated tasks. Presented at the Conference on Robot Learning in Munich, their findings highlight the transformative potential of combining advanced AI with real-world medical applications.
This innovation underscores a future where surgical robots could operate independently, guided by an extensive database of surgical expertise. As the technology evolves, it promises to redefine the standards of precision, efficiency, and accessibility in modern medicine.
The fusion of AI and robotics is poised to revolutionize healthcare, and this milestone in robotic surgery exemplifies its potential. By enabling robots to learn through observation, researchers are paving the way for a future where autonomous systems enhance surgical precision and accessibility, ultimately transforming global healthcare for the better.

