Why the latest open-weight breakthrough from the Qwen team is turning “massive compute” into a relic of the past for software engineers.
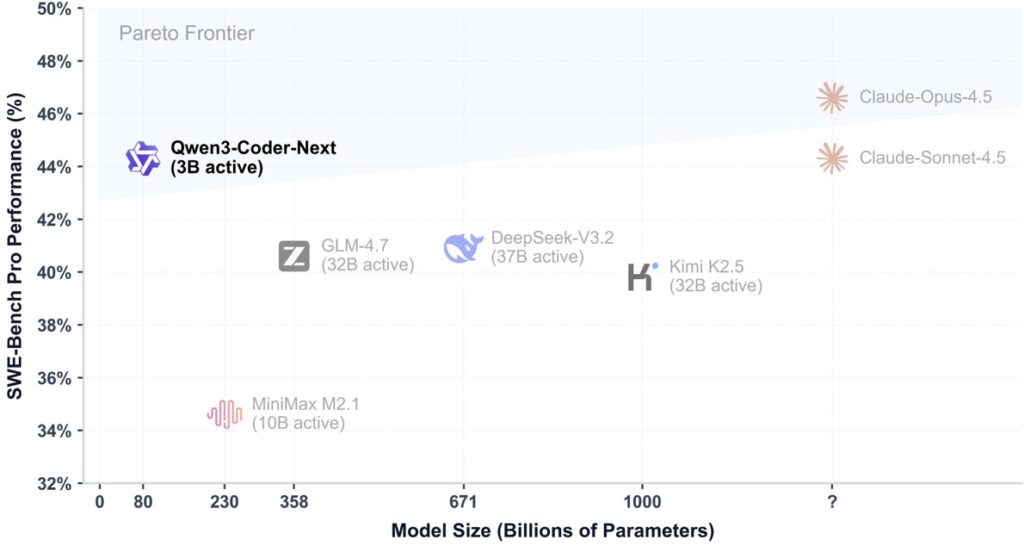
- Efficiency Meets Power: Utilizing a sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture, the model boasts 80B total parameters but activates only 3B per token, matching the performance of models 20x its size.
- Built for Action, Not Just Text: Unlike standard models, it is “agentically trained” on 800,000+ executable tasks, allowing it to plan, use tools, run code, and self-correct during complex workflows.
- Local-First Accessibility: With optimized GGUF quantizations and a 256K context window, it brings world-class “SWE-Bench” level performance to local workstations and private IDE environments.
For years, AI in coding was largely synonymous with “autofill.” We grew accustomed to ghost-text suggestions that saved us a few keystrokes. However, the Qwen team’s release of Qwen3-Coder-Next signals a definitive shift toward agentic coding. This isn’t just a model that writes snippets; it is a model designed to inhabit an IDE, navigate a file system, and fix bugs autonomously.
Built on the robust Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B backbone, this open-weight powerhouse is specifically engineered for long-horizon tasks—the kind that require a model to think like a developer, not just a translator.
Architecture: The Best of Both Worlds
The technical “secret sauce” of Qwen3-Coder-Next lies in its Hybrid Attention Plus Sparse MoE architecture. The model employs a sophisticated 48-layer layout that interweaves Gated DeltaNet (a form of linear attention) with traditional Gated Attention and MoE blocks.
By utilizing 512 total experts but only activating 10 experts plus one shared expert per token, the model maintains a lean 3B-parameter “active” footprint. This allows for rapid inference and lower memory costs—essential for long coding sessions—while the massive 80B parameter pool provides the deep, specialized knowledge required for niche programming languages and complex architectural patterns.
Trained in the Trenches
What truly sets Qwen3-Coder-Next apart is its “upbringing.” The Qwen team moved beyond static datasets, opting for agentic training at scale. The model was refined using over 800,000 verifiable, executable tasks.
During training, the model didn’t just predict the next word; it interacted with environments, executed tests, and learned from runtime failures. This reinforcement learning (RL) approach ensures that when the model encounters a “ModuleNotFound” error or a failing unit test in your local environment, it has the “muscle memory” to diagnose the issue and iterate until the code actually runs.
Shattering the “Size Matters” Myth
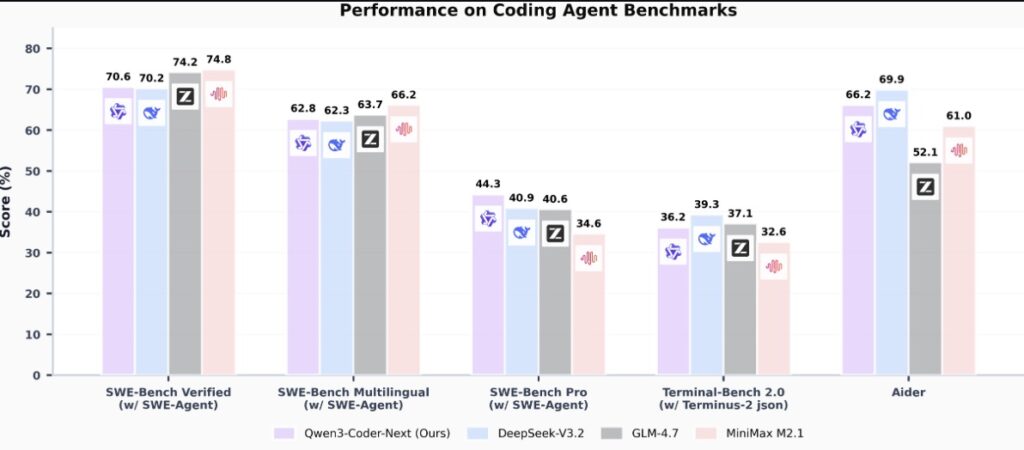
The benchmark results are, quite frankly, startling. In the world of AI, there is a long-standing assumption that more active parameters equal more intelligence. Qwen3-Coder-Next proves otherwise:
| Benchmark | Qwen3-Coder-Next (3B Active) | DeepSeek-V3.2 (671B Total) | GLM-4.7 (358B Total) |
| SWE-Bench Verified | 70.6 | 70.2 | 74.2 |
| SWE-Bench Pro | 44.3 | 40.9 | 40.6 |
| SWE-Bench Multilingual | 62.8 | 62.3 | 63.7 |
On the grueling SWE-Bench Pro, Qwen3-Coder-Next actually outperformed models with significantly higher compute requirements. It’s a clear indication that specialized, agentic training can bridge the gap created by raw scale.
Integration: A Seamless Fit for Your Workflow
The Qwen team has ensured that this model is “plug-and-play” for the modern developer. It supports a massive 256K context window, allowing it to digest entire codebases in one go. Crucially, it operates in a “non-thinking” mode, bypassing the hidden <think> blocks found in some reasoning models. This makes it an ideal engine for agent frontends like Claude-Code, Cline, or Qwen-Code, which prefer direct, actionable tool calls.
For those concerned about privacy or latency, the deployment options are flexible. Whether you are running high-throughput servers via SGLang and vLLM or utilizing Unsloth’s GGUF quantizations on a local machine with 46 GB of RAM, the barrier to entry has never been lower.
Qwen3-Coder-Next isn’t just a new model; it’s a blueprint for the future of decentralized, high-performance software engineering.

