Unveiling the Challenges and Pathways in Simultaneous Speech Translation Research
- Research Gaps Identified: Current Simultaneous Speech-to-Text Translation (SimulST) research overly focuses on pre-segmented speech, neglecting real-world complexities.
- Standardization and Solutions: The field suffers from inconsistent terminology and fragmented methods, but a unified taxonomy and framework could drive progress.
- Future Directions: Emphasizing user-centric metrics, better evaluation tools, and automated segmentation can unlock SimulST’s real-world potential.
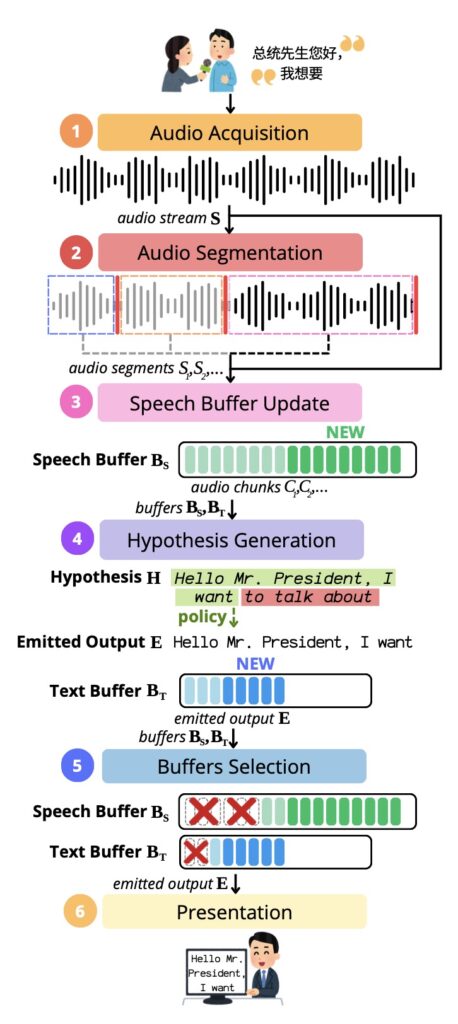
Simultaneous Speech-to-Text Translation (SimulST) aims to bridge language gaps in real-time, providing near-instantaneous translations as speakers talk. Despite its groundbreaking potential, current research predominantly focuses on pre-segmented human speech—a scenario far removed from real-world applications where speech is unbounded and unpredictable. This narrowed scope not only simplifies the challenge but also limits the practical relevance of research findings.
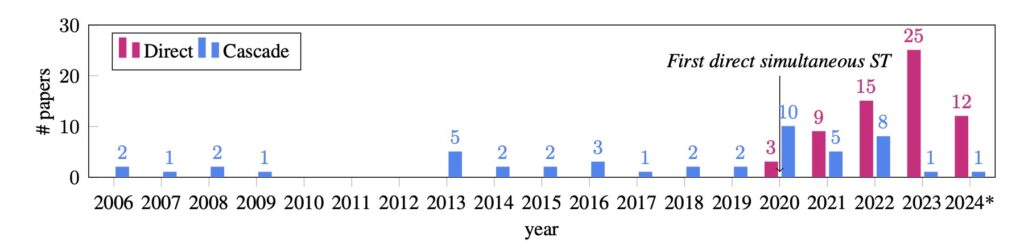
Standardizing a Fragmented Field
One of the most significant issues uncovered in a comprehensive review of 110 SimulST papers is the lack of standardized terminology and methodologies. Inconsistent definitions and metrics have created confusion, hindering meaningful comparisons between studies. To address this, researchers proposed a unified framework that defines SimulST as a six-step process. This framework identifies core components, including input strategies, system architecture, and output methods, offering a cohesive lens to evaluate and improve SimulST systems.
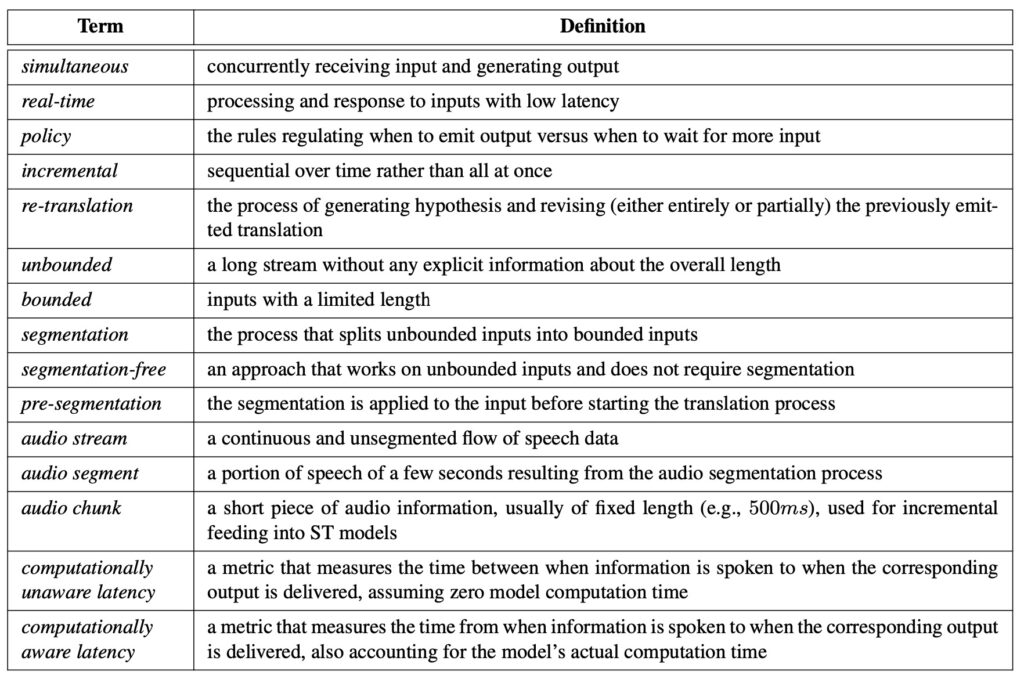
Key Challenges and Recommendations
The review highlights critical areas requiring attention. Transitioning from human-segmented to automatically segmented speech is paramount for aligning research with real-world needs. Another challenge lies in evaluation frameworks, which often fail to capture user-centric outcomes. Researchers recommend developing tools capable of handling unbounded speech and incorporating contextual information into translations. These advancements are essential for creating systems that not only perform well in controlled settings but also deliver a seamless user experience in real-world applications.
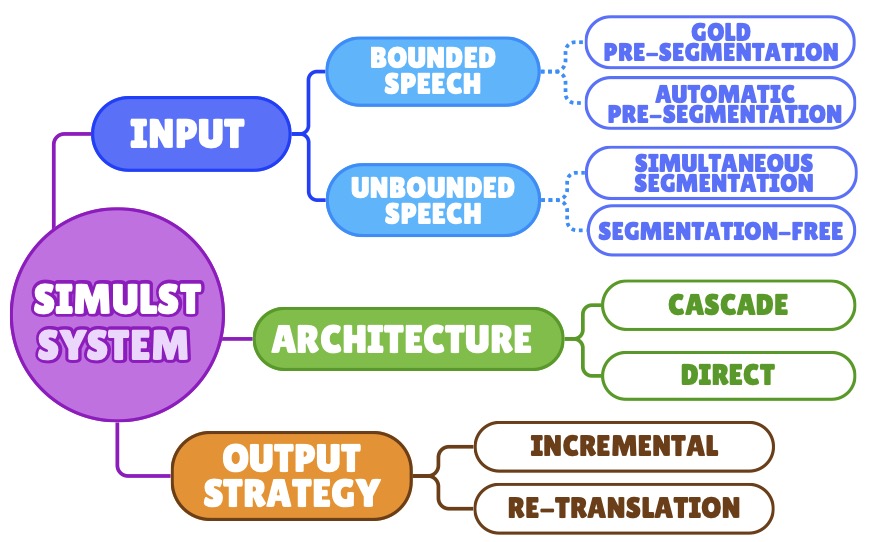
Trends and Insights from the Research Community
Analyzing trends across the field reveals a growing interest in integrating contextual and linguistic nuances into SimulST systems. However, the reliance on automatic metrics often misaligns with user experiences. Addressing this gap involves exploring novel assessment techniques that prioritize end-user satisfaction. By shifting the focus towards usability and accessibility, researchers can ensure their systems deliver practical benefits that extend beyond academic benchmarks.
Advancing SimulST technology requires collaboration and standardization within the research community. Unified terminology, robust evaluation tools, and user-focused metrics are critical to unlocking the full potential of this technology. By addressing these gaps, SimulST can evolve into a transformative tool, bridging linguistic barriers and enhancing global communication in real-time scenarios. The future of speech translation depends on building systems that are not only technically sophisticated but also practical and user-friendly.
