Bridging the Gap Between AI Autonomy and Human Control for Safer, Smarter Collaboration
- Empowering Human-AI Synergy: Magentic-UI introduces a human-in-the-loop approach that combines AI’s efficiency with human oversight, addressing the limitations of fully autonomous agents in complex tasks like web browsing, coding, and research.
- Innovative Interaction Mechanisms: The platform features six key ways for users to engage with AI agents—co-planning, co-tasking, multi-tasking, action guards, and long-term memory—making collaboration intuitive, low-cost, and effective.
- Prioritizing Safety and Evaluation: Through rigorous testing, including red-teaming for adversarial scenarios, Magentic-UI demonstrates enhanced security, while evaluations across benchmarks highlight its potential to boost productivity and reduce risks in real-world applications.
In the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence, large language models (LLMs) are powering AI agents that can tackle intricate, multi-step tasks with remarkable autonomy. Imagine an AI that browses the web, writes code, or even conducts research—all on its own. Tools like Operator, Claude Computer Use, OpenHands, GitHub Copilot, Devin, and DeepResearch exemplify this trend, enabling agents to interact with live browsers, edit codebases, submit pull requests, or sift through hundreds of webpages to generate reports. These tasks, which can span minutes to hours, promise to automate tedious work and skyrocket productivity. Yet, as exciting as this sounds, these autonomous agents often stumble in real-world scenarios, falling short of human-level performance in domains such as browser use, computer operations, software development, general and scientific research, and customer support.
The challenges are multifaceted. Agents struggle with ambiguity, misalignment with human intentions, and vulnerabilities to adversarial manipulation. For instance, they might take irreversible actions, violate user preferences, or expose private data due to misaligned behaviors or attacks like prompt injections. Recent studies highlight these gaps: agents underperform on benchmarks like SWE-Bench for coding, tasks requiring multimodal understanding (such as video data), or those needing long sequences of web actions. Moreover, as agents interact more directly with the external world, they open new attack surfaces, including phishing-like scenarios where they could be tricked into entering sensitive information on impostor sites. This raises serious safety and security concerns, potentially leading to harmful outcomes if not addressed.
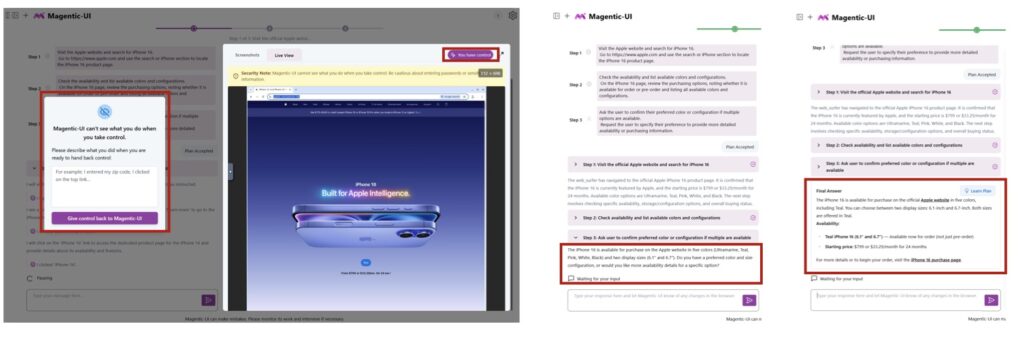
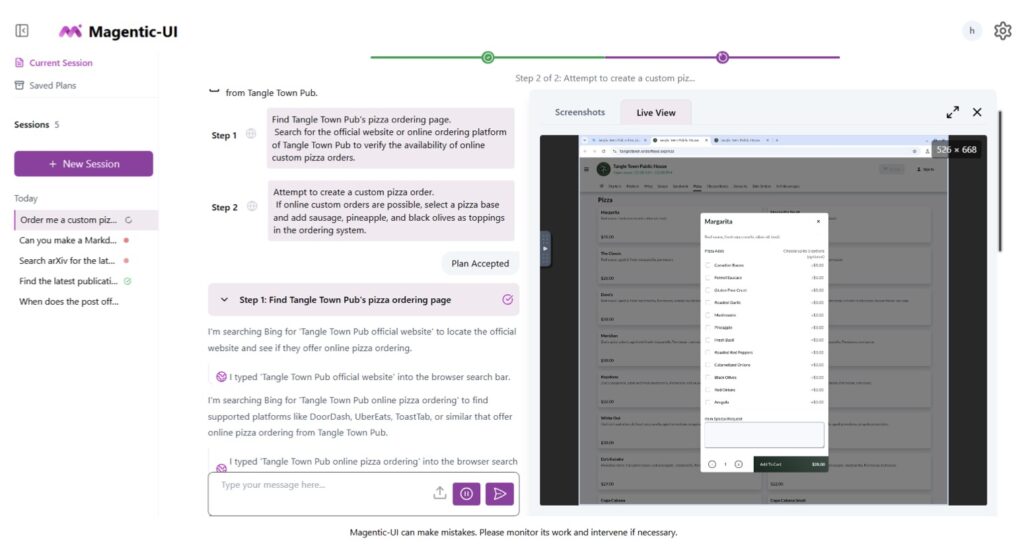
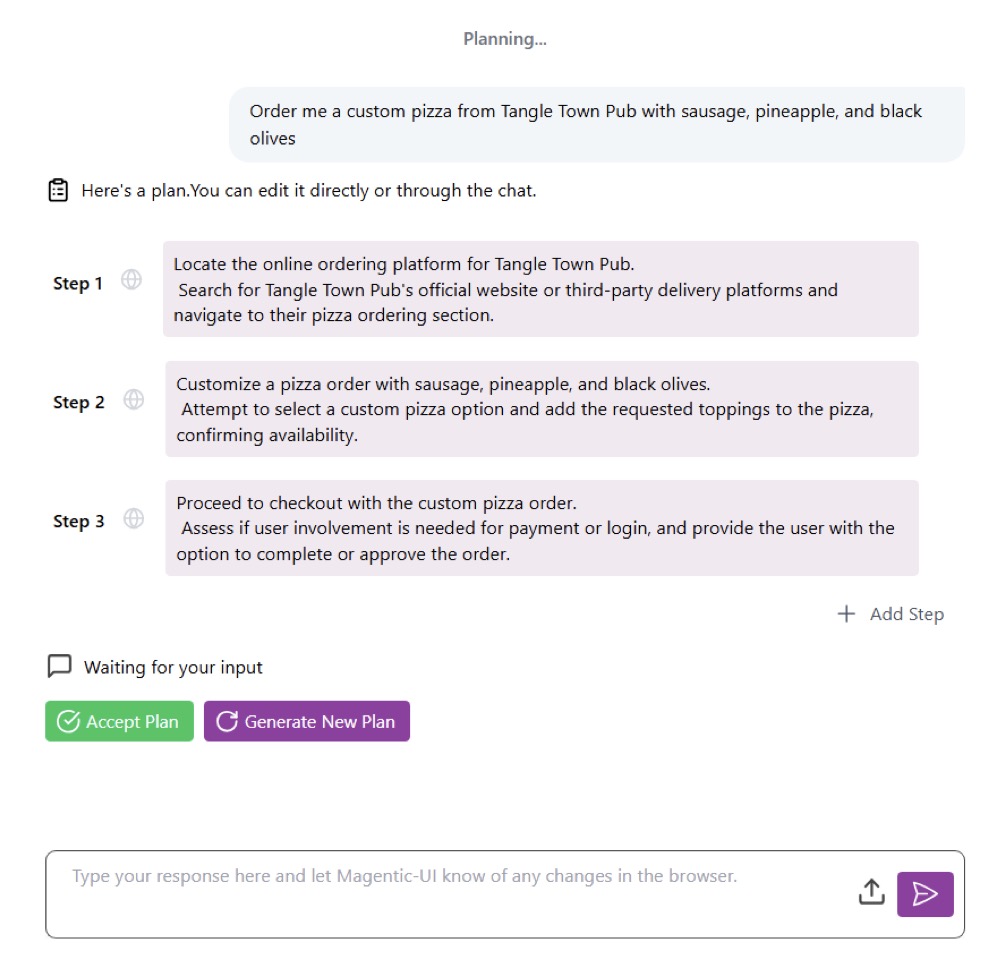
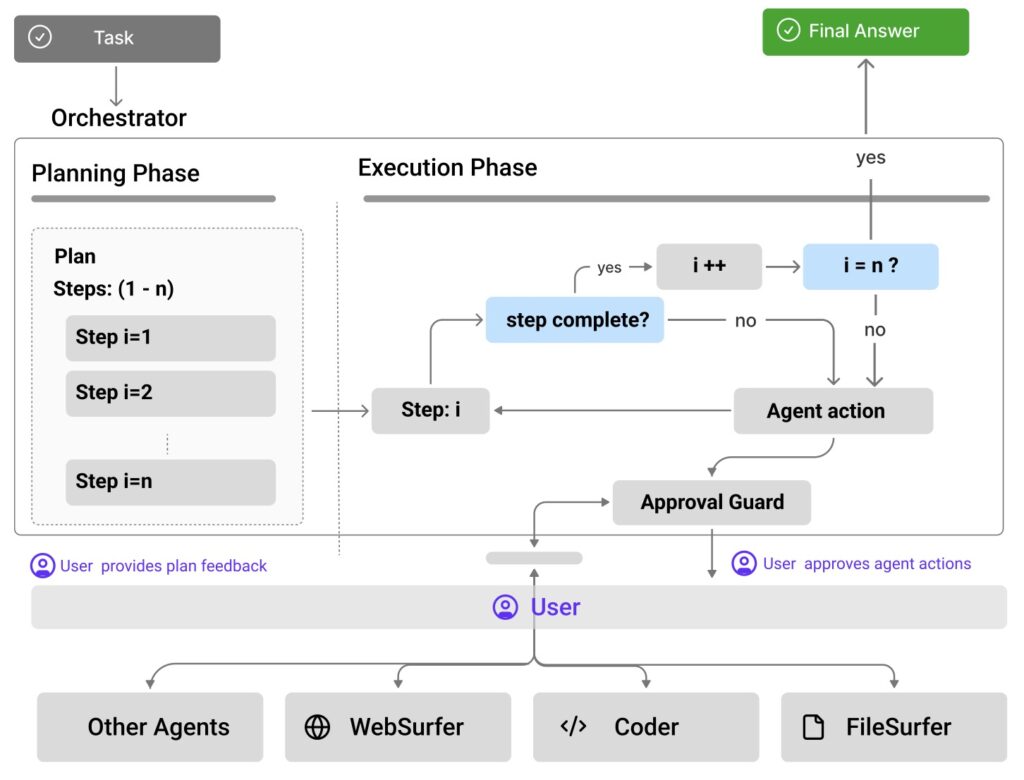
Enter Magentic-UI, an open-source web interface designed to flip the script by placing humans firmly in the loop. Rather than viewing human oversight as a mere safety net, Magentic-UI integrates it as a foundational principle, combining AI’s speed and efficiency with human judgment to create safer, more reliable systems. Built on a flexible multi-agent architecture, it supports essential tools like web browsing, code execution, and file manipulation, and can be extended with diverse capabilities via the Model Context Protocol (MCP). This setup allows users to harness imperfect AI agents productively, mitigating risks while unlocking their full potential. From the outset, Magentic-UI emphasizes transparency: every action begins with a planning phase where proposed steps are reviewed and approved by the user. Users can pause, modify, or interrupt at any time, and for high-impact actions—like navigating to a new domain—the system proactively seeks confirmation.
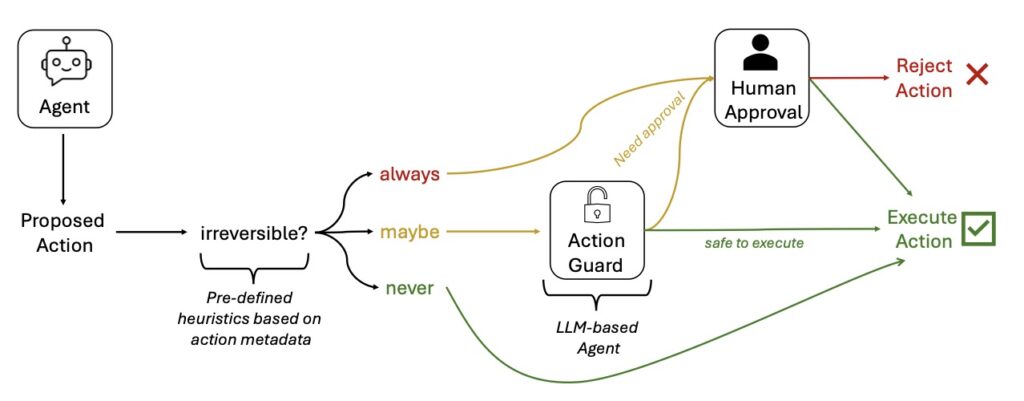
What sets Magentic-UI apart are its six innovative interaction mechanisms, crafted for effective, low-cost human involvement. Co-planning lets users collaborate on task strategies before execution; co-tasking enables joint problem-solving in real-time; multi-tasking handles parallel operations with oversight; action guards act as customizable safeguards against risky moves; and long-term memory ensures continuity across sessions. Users can even configure the system to always request permission before any action, reinforcing control. A standout safety feature is the allowed websites list, which restricts automatic visits to pre-approved sites. If the agent needs to venture elsewhere, it must provide the exact URL, page title, and rationale for user approval. This human-in-the-loop (HIL) philosophy not only minimizes unintended behaviors but also addresses broader issues like factual errors, fabrications, or biases inherited from underlying LLMs.
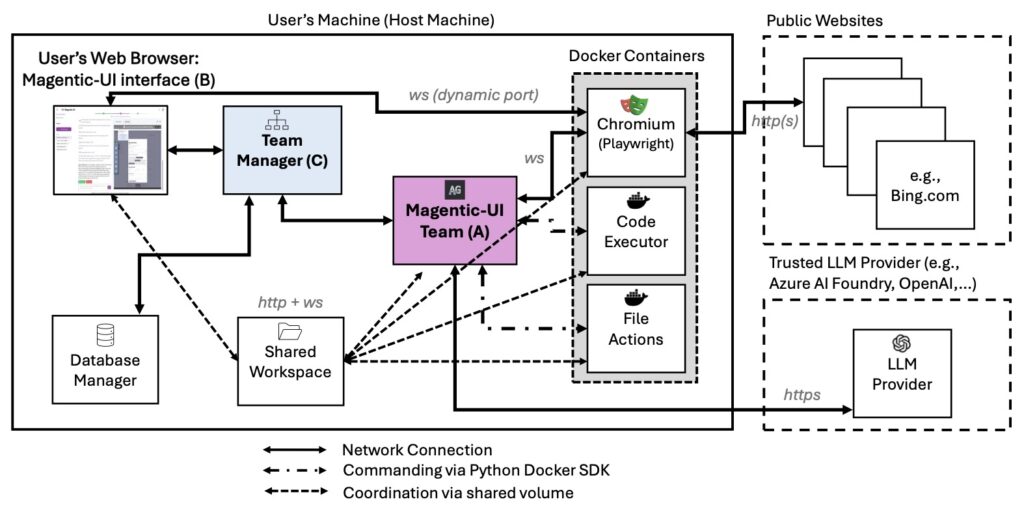
Safety is woven into Magentic-UI’s core architecture. Every component runs in isolated Docker containers, providing fine-grained access controls and shielding the host environment from agent activities. Sensitive data, including chat history and execution logs, stays local to protect privacy. The platform underwent targeted red-teaming, simulating adversarial scenarios like cross-site prompt injections or phishing attempts. In these tests, Magentic-UI either refused malicious requests, paused for user input, or failed safely due to sandboxing—proving the effectiveness of its layered defenses. However, users are cautioned to run it strictly within Docker, limit resource access, and avoid sharing sensitive data. Outputs should always be scrutinized, as the system can hallucinate or be misled by deceptive online content. Developers are encouraged to pair it with robust LLMs like those from Azure OpenAI, which include ongoing responsible AI mitigations.
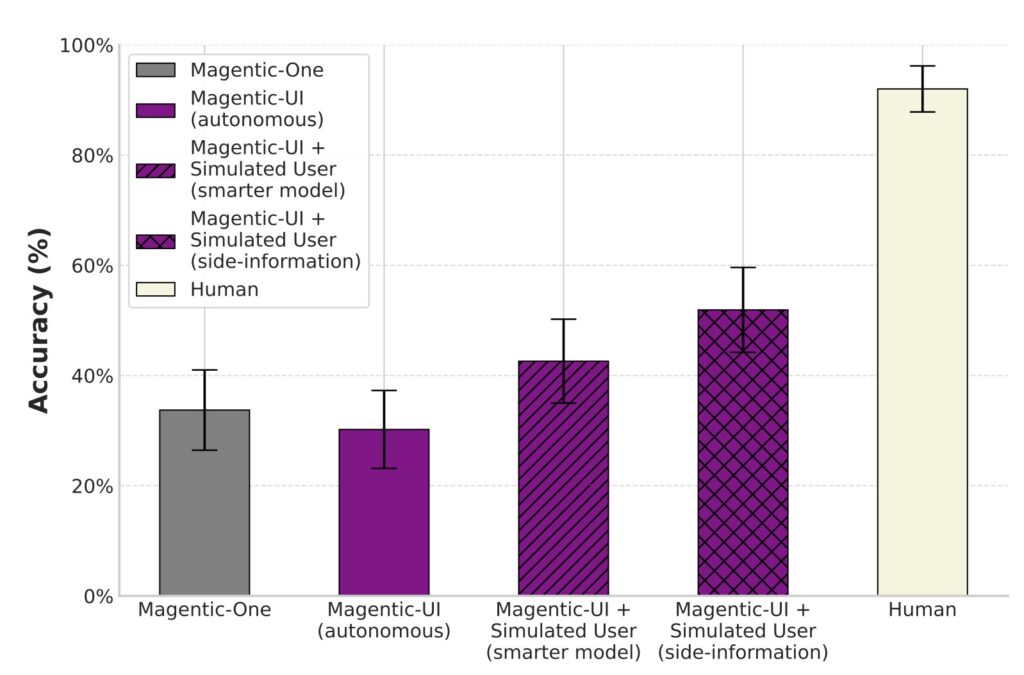
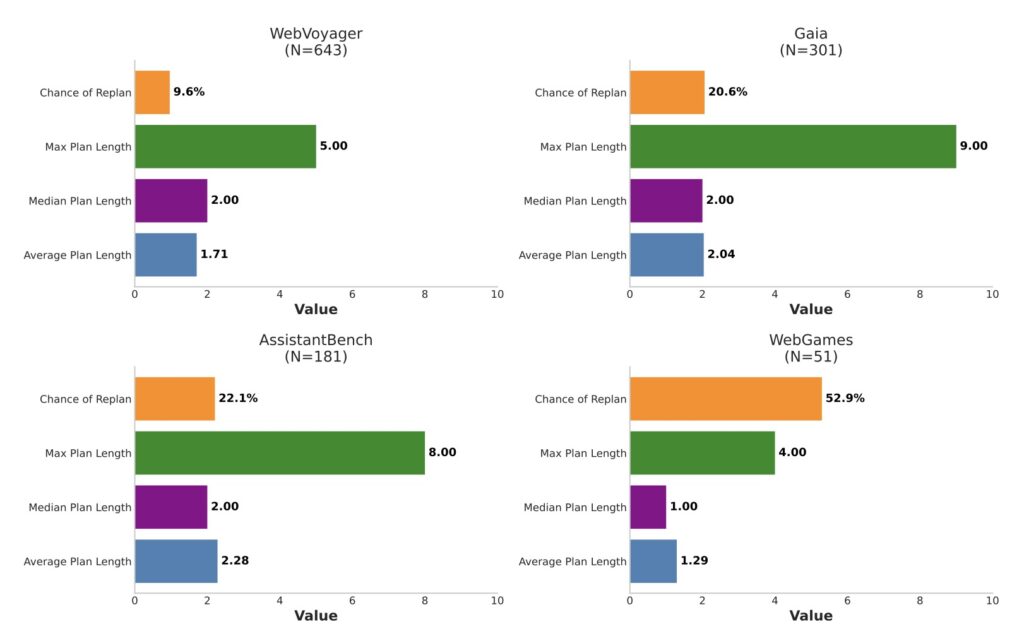
Evaluations of Magentic-UI span four key dimensions, underscoring its promise. On autonomous task completion, it performs comparably to systems like Magentic-One but lags in advanced coding, multimodal tasks, or extended web sequences—highlighting areas for improvement. Simulated user testing validated its interaction capabilities, while qualitative studies with real users provided insights into usability. Targeted safety assessments confirmed its resilience against threats. Notably, Magentic-UI was designed and tested in English, with performance in other languages requiring expert assessment by native speakers. While downstream productivity benefits weren’t measured in these evaluations—something that would need long-term trials—the findings suggest significant potential for enhancing task success and reducing oversight burdens.
Looking ahead, Magentic-UI represents a pivotal step toward human-agent collaboration that is both safe and efficient. By open-sourcing the platform, its creators invite researchers to experiment, extend mechanisms, and explore new behaviors. In a world where AI agents promise transformative productivity but grapple with real-world complexities, Magentic-UI’s HIL approach offers a balanced path forward. It reminds us that true progress lies not in unchecked autonomy, but in harmonious partnerships where humans guide AI, ensuring alignment, safety, and reliability for the tasks that matter most. As we continue to push the boundaries of AI, tools like this could redefine how we work, research, and innovate—always with human agency at the helm.