Google’s ScreenAI Sets a New Paradigm for Understanding and Interacting with Digital Interfaces
- Revolutionary Vision-Language Integration: ScreenAI, leveraging Google’s advanced AI, introduces a novel approach to understanding user interfaces and infographics by combining visual cues with linguistic elements, enabling a more intuitive human-computer interaction.
- Advanced Structured Learning and Generation: Employing a two-stage training process that includes self-supervised learning and fine-tuning with human-annotated data, ScreenAI excels in tasks like question-answering, UI navigation, and content summarization, setting a new standard for AI in UX design.
- Innovative Data Annotation and Task Generation: Through its unique Screen Annotation task and the use of large language models for synthetic data creation, ScreenAI can generate diverse and realistic user interaction scenarios, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in digital interface comprehension.
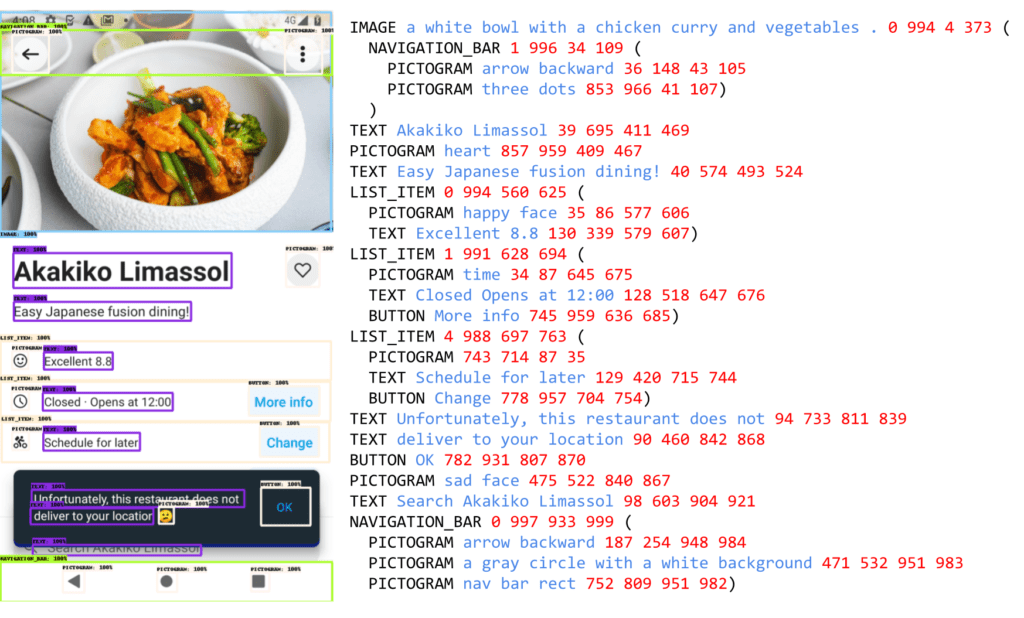
In the realm of digital communication, user interfaces (UIs) and infographics stand as crucial elements that bridge the gap between complex data and human understanding. Recognizing the inherent similarities and design principles shared by these visual languages, Google AI has introduced ScreenAI, a pioneering Vision-Language Model (VLM) designed to revolutionize our interaction with digital interfaces.
A Leap in UI Understanding
At its core, ScreenAI represents a significant leap forward in the field of AI and user experience design. By harnessing the flexible patching strategy from pix2struct and the multimodal capabilities of the PaLI architecture, ScreenAI introduces an innovative approach to visual language understanding. This model is adept at identifying and interpreting UI elements, ranging from buttons and icons to charts and tables, without the need for explicit clothing types or mask conditioning.
Bridging Visual and Linguistic Domains
What sets ScreenAI apart is its ability to seamlessly integrate visual perception with linguistic understanding. The model operates on a structured latent space, enabling it to generate annotations that describe UI elements in detail. These annotations serve as a foundation for creating training datasets for a variety of tasks, including question-answering, UI navigation, and screen content summarization.
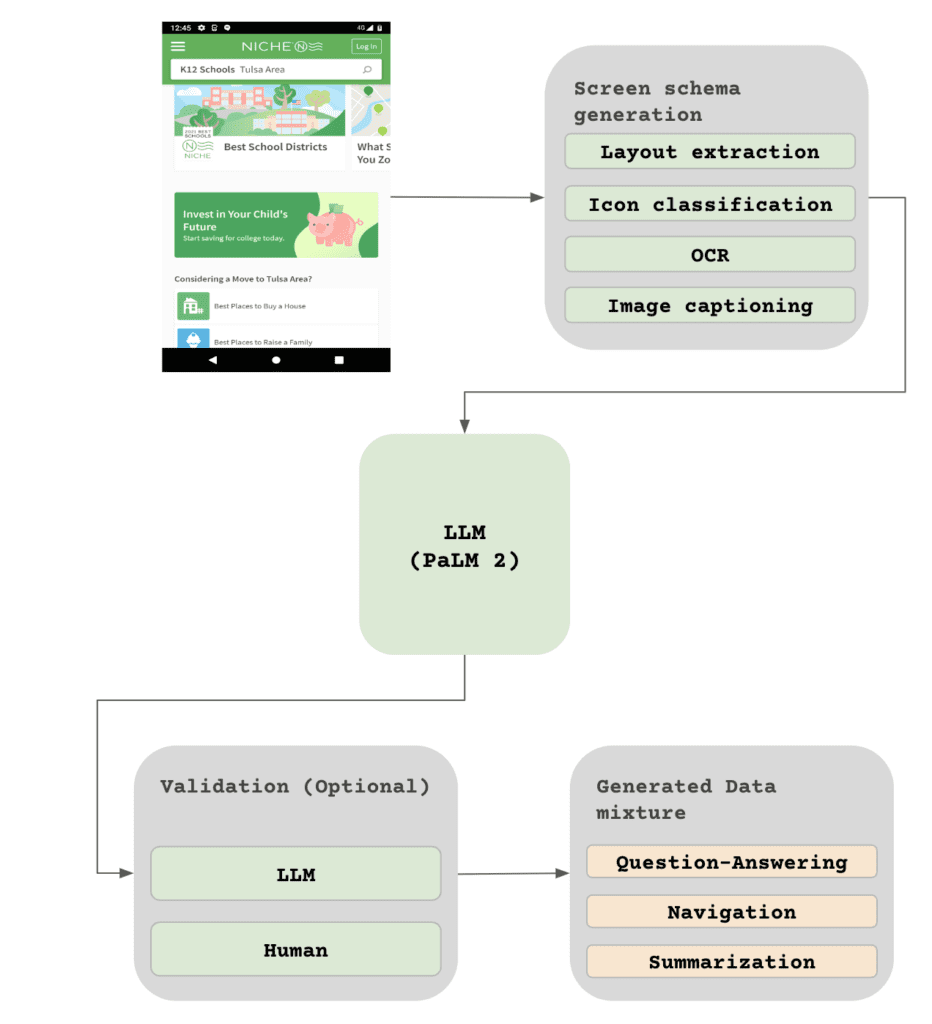
Empowering Realistic Interaction Scenarios
Through its novel data generation process, ScreenAI leverages large language models like PaLM 2 to craft realistic input-output pairs that mimic actual user interactions. This process involves intricate prompt engineering and results in a rich set of synthetic data that enhances the model’s ability to handle real-world tasks. From answering questions about a screenshot’s content to executing navigational commands and summarizing information, ScreenAI demonstrates an unprecedented level of competency in understanding and interacting with digital interfaces.
Setting New Benchmarks
The efficacy of ScreenAI is underscored by its state-of-the-art performance across various UI- and infographic-based tasks, as well as its competitive results in chart question-answering and document visual question-answering challenges. Moreover, the introduction of three new datasets aimed at evaluating layout understanding and QA capabilities further solidifies ScreenAI’s position at the forefront of this technological evolution.
ScreenAI heralds a new era in digital interface design, where AI-driven understanding and interaction open up new avenues for creating more intuitive and user-friendly digital environments. As we stand on the brink of this transformation, ScreenAI not only showcases the potential of integrating vision and language in AI but also promises to redefine our interaction with the digital world, making it more accessible and engaging for users worldwide.
