A look at the first unified model capable of separating complex audio mixtures through text, visual, and temporal prompts.
- Unified Multimodal Isolation: SAM Audio sets a new standard by isolating specific sounds—whether speech, music, or general effects—from complex mixtures using intuitive text, visual, or time-span prompts.
- Generative Architecture: Powered by a flow-matching Diffusion Transformer within a DAC-VAE latent space, the model generates high-quality audio for both the target sound and the residual background.
- The Power of PE-AV: The system is underpinned by the new Perception Encoder Audiovisual (PE-AV), a massive data engine trained on over 100M audio-video pairs to master cross-modal understanding.

The auditory world is a chaotic landscape. In any given moment, the hum of traffic mixes with a street musician’s guitar, the chatter of pedestrians, and the distant siren of an ambulance. For years, digital audio technology has struggled to untangle these complex acoustic webs. Traditional noise suppression could dampen background fuzz, but isolating specific elements with precision has remained a formidable challenge. This changes with the introduction of SAM Audio, a groundbreaking unified model that is poised to revolutionize how we interact with and manipulate sound. By sharing this technology with the community, researchers are empowering creators to explore new forms of expression and build applications that were previously out of reach.

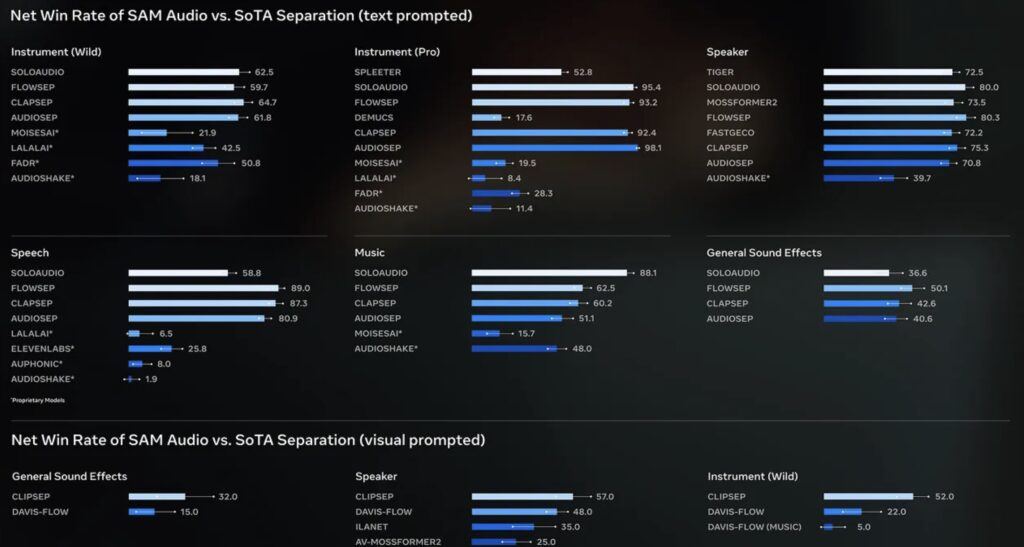
SAM Audio represents a significant advancement in audio separation technology, fundamentally shifting the paradigm from simple filtering to intelligent extraction. It is the first unified model designed to isolate any sound from complex audio mixtures using a variety of intuitive inputs. Whether a user provides a text description (like “acoustic guitar”), a visual cue, or a specific time span, SAM Audio can surgically extract the desired audio. Outperforming previous models across a wide range of benchmarks, it achieves beyond state-of-the-art performance for all prompting capabilities. This versatility allows users to isolate general sounds, music, and speech with equal efficacy, effectively solving the “cocktail party problem” for the digital age.

Under the hood, SAM Audio is not merely a filter; it is a generative separation model. It operates by extracting both the “target” (what you want) and the “residual” (everything else) stems from the original mixture. This process is powered by a sophisticated flow-matching Diffusion Transformer that operates within a DAC-VAE (Descript Audio Codec – Variational Autoencoder) latent space. This architecture enables the high-quality joint generation of target and residual audio, ensuring that the isolated sound is crisp and the remaining background is preserved without artifacts. This generative approach allows for a level of fidelity and coherence that discriminative models often fail to achieve.
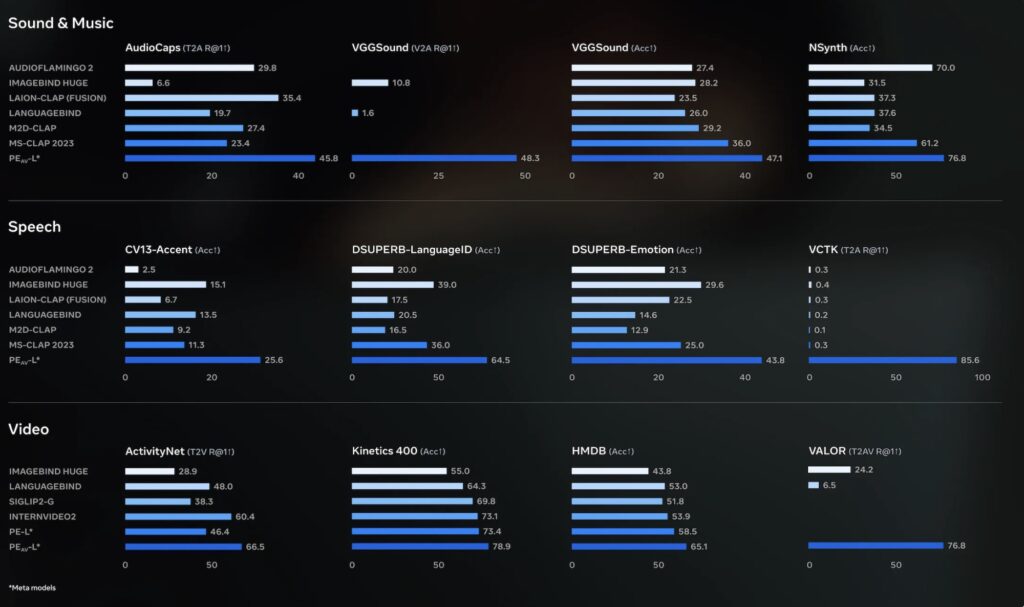
The intelligence behind SAM Audio is driven by a new family of encoders known as Perception Encoder Audiovisual (PE-AV). To truly understand sound, a model must understand the context in which sound occurs. PE-AV extends representations to audio and natively supports joint embeddings across audio–video, audio–text, and video–text modalities. This was unlocked by building a robust audiovisual data engine capable of synthesizing high-quality captions for O(100M) audio–video pairs. Unlike prior work that often suffered from single-domain limitations, this data includes speech, music, and general sound effects, providing large-scale supervision that is consistent across all modalities.
The training of PE-AV exploits ten pairwise contrastive objectives, a method that significantly strengthens alignment and improves zero-shot performance by scaling cross-modality and caption-type pairs. This unified cross-modal embedding system enables novel tasks that go beyond simple separation, such as speech retrieval, where the model can find specific spoken segments based on context. To further refine this capability, the researchers developed PE-A-Frame, a version of the model fine-tuned with frame-level contrastive objectives. This allows for fine-grained audio-frame-to-text alignment, essential for precise tasks such as sound event detection, where knowing exactly when a sound occurs is just as important as what the sound is.
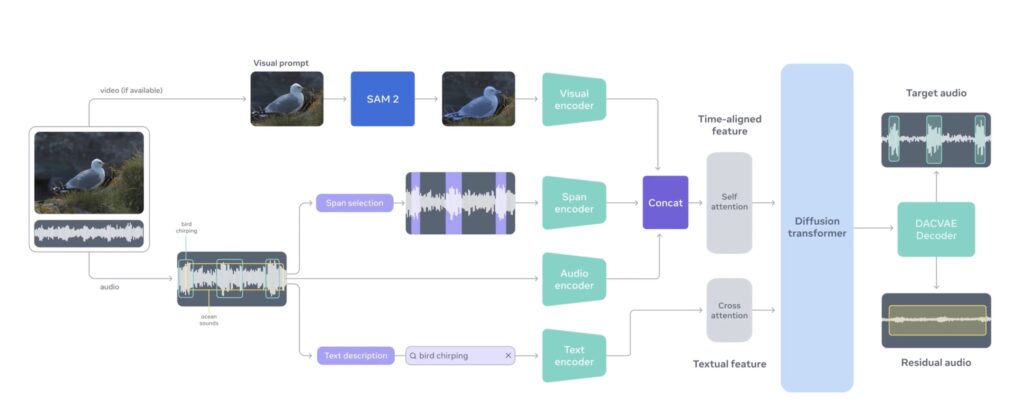
By combining the generative power of the Diffusion Transformer with the deep contextual understanding of PE-AV, SAM Audio stands as a state-of-the-art multimodal tool. It does not simply process data; it perceives it. With the release of the model, the perception encoder, and the accompanying research papers, the path is now open for developers and artists to harness these tools. From post-production in film to advanced accessibility tools and next-generation music production, SAM Audio creates a future where the complex mixture of the real world can be deconstructed and reimagined with a simple prompt.

