How a Transformer-Based Approach and Spatial Memory are Revolutionizing Dense 3D Reconstruction.
In the rapidly evolving field of 3D reconstruction, the introduction of Spann3R marks a significant leap forward. Here’s a quick overview of how this cutting-edge approach is reshaping the landscape:
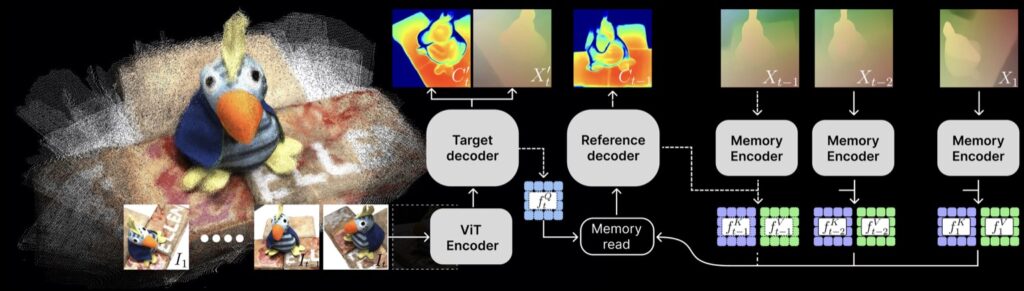
- Revolutionary Architecture: Spann3R leverages a transformer-based architecture to predict global 3D pointmaps directly from images, eliminating the need for prior knowledge about the scene or camera parameters. This stands in stark contrast to previous methods like DUSt3R, which relied on local coordinate frames and optimization-based global alignment.
- Spatial Memory Innovation: Central to Spann3R’s approach is its external spatial memory, which tracks and encodes 3D information across frames. This allows the model to generate accurate 3D structures for new frames by querying past data, enabling real-time processing and seamless incremental reconstruction.
- Enhanced Performance and Future Directions: Trained on diverse datasets, Spann3R demonstrates robust performance and generalization capabilities. However, challenges remain, including large-scale scene reconstruction and integration of bundle adjustment techniques. Future work will focus on scaling the model, improving accuracy through advanced training methods, and exploring self-supervised learning from casual videos.
In the quest for more accurate and efficient 3D reconstruction, Spann3R emerges as a game-changer. This innovative model integrates the power of transformers with a novel spatial memory system to deliver high-quality, real-time 3D reconstructions from RGB images. By sidestepping the need for test-time optimization and leveraging learned 3D information, Spann3R paves the way for future advancements in scene reconstruction technology. As research continues, the model’s ability to handle larger-scale scenes and incorporate traditional adjustment techniques will be crucial in overcoming current limitations and achieving even greater accuracy.