A deep dive into the Nemotron-Nano-3-30B-A3B-NVFP4 architecture and the new standard for efficient inference
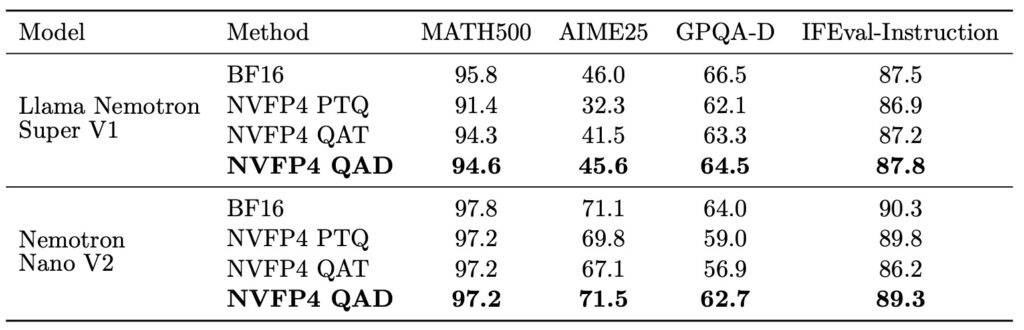
- Accuracy Recovery via QAD: NVIDIA’s Quantization-Aware Distillation (QAD) successfully restores NVFP4 quantized models to near-BF16 accuracy levels, overcoming the stability issues found in traditional Quantization-Aware Training (QAT).
- Hybrid Architecture Efficiency: The Nemotron-Nano-3-30B-A3B model utilizes a hybrid Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) and Mamba-2 architecture, allowing it to have 30 billion total parameters while only activating 3.5 billion per token for high efficiency.
- Data Composition and Demographics: Analysis of the training datasets reveals that 64-99% of samples lack demographic identifiers; however, within samples containing such terms, “White” is the most frequent ethnic identifier (43-44%), necessitating specific mitigation strategies.
The pursuit of efficient Large Language Models (LLMs) often involves a trade-off: reducing the precision of the model to save memory and increase speed usually results in a degradation of intelligence. This technical overview examines NVIDIA’s solution to this problem—Quantization-Aware Distillation (QAD)—and analyzes the architecture and training data of the resulting model, the Nemotron-Nano-3-30B-A3B-NVFP4.
Quantization-Aware Distillation (QAD)
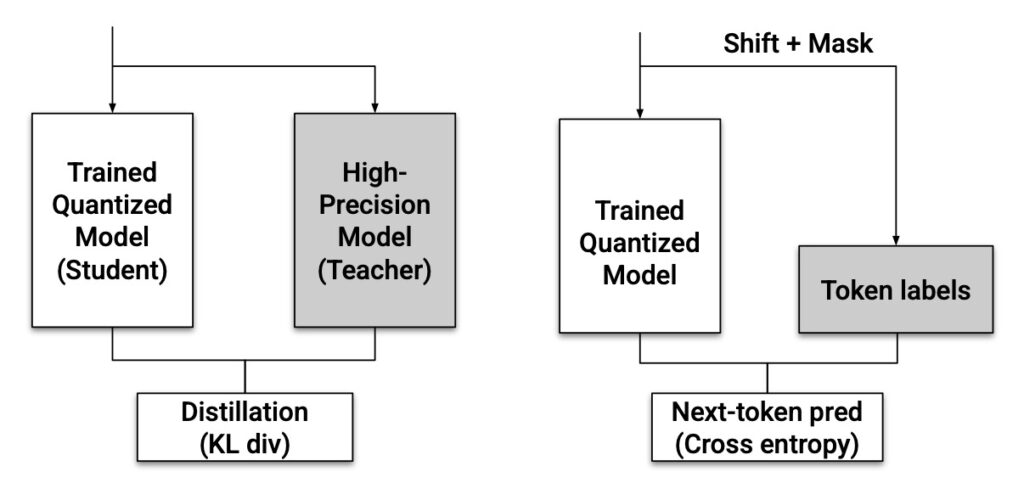
Quantizing a model from high precision (BF16) to lower precision (NVFP4) typically introduces “noise” that confuses the model. While Quantization-Aware Training (QAT) has been the traditional fix, it suffers from engineering complexity and instability.
NVIDIA’s report highlights QAD as a superior alternative for recovering accuracy. QAD functions by distilling a full-precision “teacher” model into a quantized “student” model using a KL divergence loss. This process yields two specific advantages for modern LLMs:
- Stability in Complex Pipelines: QAD remains effective even for models that have undergone multi-stage post-training, such as Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), Reinforcement Learning (RL), and model merging.
- Data Robustness: Unlike methods that require the original training data, QAD is robust to data quality and coverage. It can recover accuracy using partial-domain data, synthetic data, or even when trained on random tokens.
Evaluations across the Nemotron family (including AceReason, Nano V2, and Llama Super v1) show that QAD consistently brings the quantized student model back to near-BF16 accuracy levels.
Model Architecture: The Hybrid Approach
The Nemotron-Nano-3-30B-A3B-NVFP4 is designed as a unified model for both reasoning and general chat tasks. It supports English, German, Spanish, French, Italian, and Japanese, alongside 43 programming languages.
The model employs a distinctive hybrid architecture comprising 52 total layers:
- 23 Mamba-2 Layers: Utilizing State Space Models (SSM) for efficient sequence modeling.
- 23 Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) Layers: Each layer contains 128 routed experts plus 1 shared expert.
- 6 Attention Layers: Utilizing Grouped Query Attention (GQA).
This configuration allows for massive scale with efficient execution. While the model houses 30 billion parameters in total, only 3.5 billion parameters are active per token. The system activates 6 experts per token, optimizing computational resources without sacrificing the breadth of knowledge contained in the full parameter set.
Configurable Reasoning
A key feature of this model is its “thought process.” It is trained to generate a reasoning trace before concluding with a final response. This is configurable via a flag in the chat template:
- Reasoning Enabled: Generally results in higher-quality solutions for complex queries.
- Reasoning Disabled: Provides immediate final answers, offering lower latency but with a slight decrease in accuracy for difficult prompts.
The Four-Stage Training Pipeline
The creation of the Nemotron-Nano-3-30B-A3B involved a rigorous four-stage process using the Warmup-Stable-Decay (WSD) learning rate schedule (peak rate 1e-3).
- Pre-Training (25 Trillion Tokens): Using Megatron-LM, the model was trained on a massive corpus of code, math, science, and general knowledge.
- Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT): The model was fine-tuned on synthetic data covering tool calling, instruction following, and structured outputs.
- Reinforcement Learning (RL): This stage utilized Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) and RLHF with a generative reward model to refine conversational quality and multi-step reasoning.
- Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) & QAD: The model was quantized to NVFP4 with the KV Cache in FP8. To preserve performance, a selective strategy kept attention layers and specific Mamba layers in BF16. QAD was then applied to recover any accuracy lost during this compression.
Dataset Demographics and Statistical Composition
The training data for Nemotron models includes high-quality curated and synthetically generated datasets like FinePDFs, EssentialWeb, HotpotQA, and SQuAD. An analysis of this data reveals specific statistical distributions regarding demographic representation.
In the majority of the data (between 64% and 99% of samples depending on the specific source), there are no explicit mentions of demographic classes such as age, gender, or ethnicity.
However, in the subset of data where demographic terms are present, specific skews were identified:
- Gender: References to “male” subjects outnumber references to “female” subjects.
- Ethnicity: In document-based datasets like FinePDFs and EssentialWeb, “White” is the most frequent ethnic identifier, comprising 43% to 44% of all ethnicity mentions.
To address these imbalances, the development team recommends and implements mitigation strategies, including bias audits and counterfactual data augmentation, to align the model with desired behavioral standards.
Synthetic Data and Quality Control
To supplement real-world data, NVIDIA utilized a synthetic data generation pipeline. This involved distilling trajectories and solutions from larger, permissive models (like GPT-OSS-120B) for math, code, and science tasks.
Strict filtering was applied to ensure quality:
- Structural Checks: Discarding malformed examples (e.g., missing tool definitions).
- Repetition Filtering: Removing reasoning traces that exhibited “pathological repetition” (repeated n-grams), which indicates low-quality logic.
- Content Moderation: Internal audits revealed that some teacher models occasionally produced content promoting specific nationalistic narratives or political entities. Targeted keyword and regex-based filters were deployed to remove these trajectories entirely.