New NLP task and dataset set the stage for improved information extraction and generation
In the new paper WebBrain: Learning to Generate Factually Correct Articles for Queries by Grounding on Large Web Corpus, researchers introduce a new NLP task called WebBrain, which aims to generate short, factual articles with references for queries by mining supporting evidence from the web. The ultimate goal is to create a fluent, informative, and factually correct short article, such as a Wikipedia entry, for a factual query not currently covered in Wikipedia.
Key Points:
- WebBrain introduces a new NLP task focused on generating short, factual articles with references for queries by mining supporting evidence from the web.
- Researchers have created a large-scale dataset, WebBrain-Raw, extracted from English Wikipedia articles and their crawlable references, significantly larger than previous datasets.
- Two task-specific datasets, WebBrain-R and WebBrain-G, have been constructed for training in-domain retrievers and generators, respectively.
- The paper presents a new framework, ReGen, designed to improve the factualness of generated content by enhancing evidence retrieval and task-specific pre-training for generation.
- ReGen outperforms existing techniques in both automatic and human evaluations.
To enable experimentation with WebBrain, the researchers have constructed a large-scale dataset called WebBrain-Raw, extracted from English Wikipedia articles and their crawlable references. This dataset is ten times larger than the largest previously available dataset, making it a valuable resource for the research community.
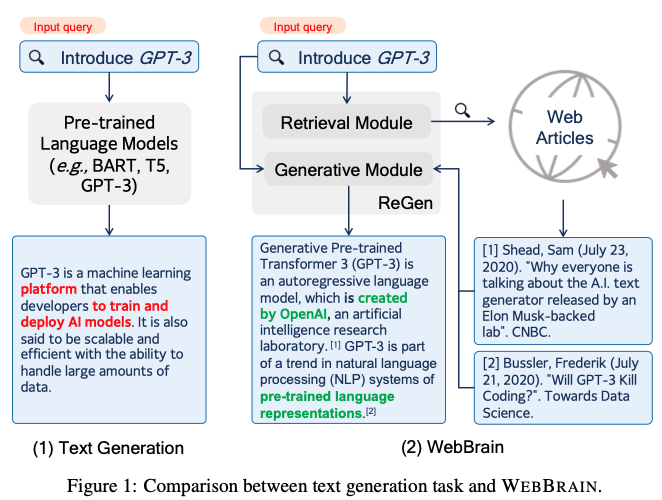
From WebBrain-Raw, the researchers have created two task-specific datasets: WebBrain-R for training in-domain retrievers and WebBrain-G for training generators. These datasets are used to develop and test various NLP techniques to tackle the WebBrain task.
The researchers found that current NLP techniques often struggle to maintain factual accuracy in the WebBrain task. To address this issue, they propose a new framework called ReGen, which enhances factualness by improving evidence retrieval and task-specific pre-training for generation. ReGen outperforms all baseline models in both automatic and human evaluations.
The introduction of the WebBrain task and the accompanying dataset opens up a new research pathway for AI models to autonomously acquire knowledge from the web and better serve human users by fulfilling a broader range of fact-oriented information needs.
